We can all agree welding has its risks, and nearly half a million welders in the US are exposed to health and safety risks every day.
If you follow proper precautions and safety tips and wear your PPE, welding can be a pretty safe occupation.

If you ignore safety measures, you increase your chances of causing fire, burns, eye injuries, or even more significant disasters and death.Organizations in the US, such as Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), offer welding safety precautions and important guidelines to keep the workers safe.
We made this article and put together all the arc welding safety tips and welding hazards provided by occupational health experts to make it easier for you and ensure you stay safe while welding.
Welding Safety Tips, Precautions, and Welding Hazards
One of the essential things during welding is ensuring the proper safety precautions. Ignoring the welding safety precautions and an appropriate PPE increases electrical shock risks, fire hazards, noise hazards, exposure to welding fumes and gases and UV and IR radiation, and other hazards.
Here is an explanation of how these most common welding hazards occur and what safety measures you need to prevent them. Keep in mind that cutting, soldering, and brazing operations produce less heat and fumes, they are less hazardous, but the welded joint between two metal objects can never be strong as one with the welding process.
| Hazard | PAWPAC Air Carbon Arc Processes | SMAW GTAW GMAW FCAW | SAW | Oxyfuel |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ergonomic | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Electric Shock | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✘ |
| Bright Light | ✓ | ✓ | (✓) | ✓ |
| Ultraviolet radiation | ✓ | ✓ | (✓) | ✘ |
| Toxic Fumes and Gases | ✓ | ✓ | (✓) | ✓ |
| Heat, Fire and Burns | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Noise | ✓ | ✘ | ✘ | ✘ |
| ✓ hazard is present, ✘ indicates no hazard, (✓) hazard is present if there is no SAW flux. | ||||
Electric Shock
The fundamental of the arc welding process is the live electrical circuits create the welding arc and a pool of molten metal between two metals. That’s why welders are at risk of electric shock. We can agree electric shock is one of the most dangerous hazards, which can cause severe damage or even cause fatalities. The electricity that flows during the welding process and electric arc should be taken seriously.
Electric shock can be primary and secondary. Primary electric shock can be lethal, as it occurs at 230 or 460 volts. Secondary voltage shock is more common, as it appears at a lower voltage once you touch the electrode circuit, where the electrical circuit happens at 20-100V. Be aware that even secondary voltage shock can injure an operator.
How to Prevent Electric Shock
To prevent and avoid electric shock, you should always keep your welding gloves dry. Sometimes it is even better to have a spare pair if you can’t keep them dry all the time.
If you do your welding operations in a laying position, you should use rubber mats, plywood, or some other dry insulation for your body. You should always insulate your body from the welded metal.
You should never rest your body, your arms, or your legs on the workpiece. Importance increases if your skin is exposed you wear wet clothing. Make sure you don’t hold a bare wire in one and a second bare wire in another hand.
Fire Hazards
Even though the heat of the welding arc between two pieces, can even reach the 10,000°F, that’s not the leading cause of fire hazard.
Fires occur when molten metals, hot slag, and sparks due to intense heat fly around your workshop.
Keep in mind that weld sparks can spray up to 35 ft. from your work, making sure there is flammable material in that area. You should always wear fire-resistant clothing.

Note that there is a difference between flame-resistant and flame retardant clothing. Flame retardant fabrics are chemically treated as slow-burning or self-extinguishing when exposed to an open flame, while inherently nonflammable materials make fire-resistant clothing.
Fire Prevention Tips
As the sparks during the welding activities fly around the workplace quickly, you should watch where they fall. If there is fuel or hydraulic lines, you’ll have to move. You should put the fire-resistant shield over the combustible substances and flammable materials if you cannot move.
If you are welding from high places or a ladder, make sure there are no flammable materials beneath you to ensure fire protection. It would be best if you always had a fire extinguisher nearby. Please make sure you check pressure gauges, to make sure it is full. In addition, notice the rest of the workers by triggering the fire alarm.
If there are no extinguishers in the area, you need a sand bucket, blankets, hoses, and other fire-resistant clothing. Wearing flame-resistant gloves is crucial, and workers that ignore them increase the risk of severe burns.
Welding Fumes and Gases
During the arc welding processes, base metals coating and fine particles from the consumables melt, creating hazardous fumes.
The damage welding fumes and gases can cause depends on the base element, structure, and length of exposure.
The most common type of welding fumes contains nickel oxides, carbon monoxide, nitrogen, ozone, sometimes even released by a stainless steel base metal.

Illnesses caused by short-term exposure to welding fumes can cause temporary effects, such as burning eyes and skin, nausea, metal fume fever, and dizziness. They usually last short, but you should stay away from long-term exposure.
Long-term exposure to welding fumes can affect pulmonary function, cause lung cancer or even reduce the sperm count.
How to Prevent Fume Exposure and Metal Fume Fever
This one is no mystery as all you need to do is not inhale the large quantities of metal fumes released by heated metals. This advice sounds easy once you put it this way, but toxic fumes can cause severe damage to your respiratory tract.
It would help if you kept the fumes out of your breathing zone and use adequate ventilation. If you can’t avoid the fume plume or provide protection by ventilation, you should opt for a welding respirator. They will prevent welders and other workers from breathing high levels of fumes. Keep in mind that local exhaust might be the best way to do it.
Noise Hazards
During ordinary welding activities, you can often hear loud noises. Loud noises are described as the ones that come above 85dB.
Long-term exposure to loud noises can lead to hearing impairment or even cause permanent damage. Noise is one of the most overlooked physical hazards, but it can be as dangerous as other welding hazards.
How to Prevent Noise Hazards
Even though the damage adds up, and you don’t notice it straight away, it is a good idea to use ear protection. Sometimes, you’ll notice hearing damage once you complete the hearing test, so make sure you wear proper ear protection all the time to prevent noise hazards.
Exposure to UV and IR Radiation
Radiation exposure can, by all means, cause severe eye damage and leave marks on your skin. Infrared radiation can cause retinal burning cataracts.
Sometimes, even brief exposure to arc rays, which emit ultraviolet light, can cause an eye burn, famous as welder’s flash. While flash is not that serious if it happens once or twice, repeated exposure to intense light can cause permanent eye damage.
How to Protect Your Eyes from Radiation
Since you have to look at the piece during the welding operation, you need to provide proper eye protection from direct UV radiation exposure.
Welding helmet, safety glasses, goggles, and hand shields are the essential welding equipment to do it.
Welding helmets have built-in filter plate and side shields which will provide proper eye protection. Welding helmets and hand shields can also provide protection from direct radiant heat.
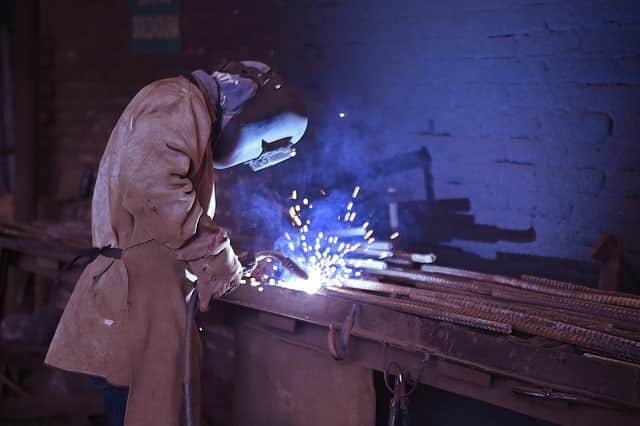

Some safety glasses and goggles also have appropriate filter lenses and side shields, but they must meet the test for transmission of radiant energy prescribed in ANSI/ISEA Z87.1-2015, American National Standard for Occupational and Educational Personal Eye and Face Protection Devices.
Besides eye damage and radiation, welding helmets and hand shields with filter plates can also protect you from physical hazards, such as particles, debris, slag chips, arc eye, chemical burns, and even falling objects.
Important Arc Welding Safety Measures and Safety Precautions
Here are some vital welding safety measures to ensure safety protection and avoid the most common welding hazards. Some of the welding hazards can be prevented by proper personal protective equipment (PPE), training, engineering controls, and work practices.
Keep in mind that all welding operations, either it is shielded metal arc welding, gas tungsten arc welding, or submerged arc welding, can cause health hazards. The most common ones are safety injuries or physical hazards, such as falling objects damaging your head. Other types are ergonomic, chemical, biological, and psychological.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Note that welders must wear protective clothing designed to protect workers from molten metal sparks, hot slag, and radiation all the time. Burns are the most common injuries among welders, and they usually happen by hot sparks falling on bare skin. Be aware that a proper PPE can significantly reduce the chances of physical hazards, and reduces a chances of injuries.
Keep in mind that various jobs require different welding equipment, but protective clothing must provide enough portability and protection at the same time.
Here is a table that represents the personal protective equipment – PPE.
| Body Part | Equipment | Protection |
|---|---|---|
| Eyes and Face | Welding helmet, Hand shield, Goggles | radiation, flying particles, hot slag, intense light, irritation and chemical burns. |
| Lungs | Welding Respirators | welding fumes and gases. |
| Exposed skin (other than feet, hands and head) | Fire/Flame Resistant Clothing Aprons | heat, fires burns, radiation. Note: Don’t wear pants with cuffs |
| Ears – Hearing | Ear Muffs Ear Plugs | noise |
| Feet and hands | Boots, Gloves | electric shock, heat, burns, fires. |
Welding Safety Precautions Training
To minimize health issues and safety injuries, increase safety, and keep you protected you should go through training that provides proper knowledge on using your safety equipment. One of the easiest ways to do it is by online courses.
OSHAcademy provides free welding safety courses, while AWS organization courses cost around $75. Keep in mind that these are as important as welding education, so don’t think twice before doing it.
Ventilation Control
Adequate ventilation is essential as it removes airborne gases and particles that are a result of welding activities.
As the welding processes can create high fume levels, sometimes you’ll have to combine a couple of ventilation types to provide proper airflow to your work area.
Adequate ventilation depends on several factors, and regarding them, it can be natural, mechanical, or local ventilation.

Natural ventilation provides air movement by natural forces. Winds usually do it outdoors, while air moves by opening the windows inside. According to OSHA, a room with listed specifications fits the standards of natural ventilation:
- The room or a work area that contains 10,000 cubic feet (about 22 x 22 x 22 ft.) for each worker
- The ceiling must be more than 16 feet high.
- Welding equipment cant block the airflow
- Welding isn’t done in a confined space.
Rooms that don’t offer provided specification must use mechanical ventilation or 2000 cfm of air for each welder. This requirement differs if welders use air welding respirators, local exhaust welding helmets.
Local ventilation captures the welding fume near the electric arc, keeping it away from other workers’ breathing zones in the welding area, and filters the contaminants out of the air. Keep in mind that engineering controls, such as ventilation do not eliminate the source of hazard. They are just designed to protect workers from it. Proper ventilation will permanently eliminate possible oxygen deficiency, not only to a welder nearby but also to all the vicinity operators.
Inspection and Maintenance of Equipment
To increase your safety, before you start your arc welding operation, you should take some time to inspect your equipment and electrode holder. The inspection takes only 5-10 minutes, but it can be constructive. If you notice any irregularities, you should first repair welding equipment and start welding activities.
It would be best if you started by:
- Reading the instruction manual provided by the welder manufacturer
- Read the warnings and instructions on the equipment nameplates and decals, as well as consumables labels and material safety data sheet.
Before you turn on your welder, you should:
- Make sure all connections are tight, including the earth ground
- Make sure electrode holder, and welding cable are well insulated and in good conditions
- Make sure your settings are suitable for the job you’re about to do
When approaching the engine-driven welder, you should:
- Make sure it’s running fine, and all hoses and connections are tight
- Check the fuel cap and look for the fuel and oil leakage
- Try not to spill fuel when refueling
- Pay attention to the enclosure and fan guarding it, make sure they are in place
Before you start your welding work, you should make sure that:
- All work area conditions are normal (ventilation, respirator, safety equipment).
- When working on job sites, if it is required, get the required permits
- If you are working in a confined space and cramped conditions, make sure you respect the special OSHA regulation and job site requirements and keep the fume plume out of your breathing zone
- If you notice anything wrong, make sure to repair welding equipment before doing any welding work
Workplace Cleaning and Cable Management
Even though maintaining and inspecting the equipment is essential, keeping the workplace clean is crucial. To protect workers around you, you need to keep your cables, cylinders, and other equipment out of the traffic area.
Proper cable management increases your productivity but also prevents injuries of welding operators passing by. You should also use protective screens, just if someone walks by while sparks, grinding fragments, or other metal objects are flying around.

Therefore, a good practice is to avoid clutter and keep your workplace as clean as possible. That way, you increase the safety measures and eliminate the chances of debris injuring employees around you.
Gas Cylinder Storage and Use
You must pay particularly close attention to cylinder storage, and use since the high pressure they hold can cause explosions. You need to inspect them before use, just like you did with the other equipment.
Gas cylinders must be secured in an upright position, and all the valve caps need to be in a place. You should store it in an area far from flammable materials and fuels and ensure it is safe from damage, heat, and fire.
When welding, to minimize fire and explosion risk, keep the cylinder out of traffic areas, sparks, and flammable material.

It would be best if you didn’t allow the electrode or the electrically hot part of the welder to touch the cylinder. You can prevent the dust and dirt from damaging the regulator by cracking the valve open. When opening the cylinder valve, you should always face it away from the source of ignition.
Electric and Magnetic Fields – EMF
When the electric current flows through any conductor, it causes localized Electric and Magnetic Fields (EMF). Welding current creates those fields around cables and welding machines.
Electric and Magnetic fields can interfere with a pacemaker and other devices, so the operator wearing one must be aware of it and consult the physician before welding. Besides pacemakers, EMF fields safety hazards are yet to be explored.
First Aid Kit and Fire Extinguishers
Workers should always have a well-stocked first aid kit, fire-resistant blanket, and a filled fire extinguisher in a workplace. One of the workers should get proper first aid knowledge to treat the minor injury that occurs. Be aware that serious injuries such as chemical burns or poisoning by carbon monoxide, nickel oxides, chromium oxides, or other invisible gaseous fumes and airborne contaminants should be treated by trained medical personnel.
To help with fire prevention, you should always keep suitable fire extinguishing equipment, such as a bucket of sand or dry chemical extinguishers of the ABC type. The extinguisher should be filled and large enough to handle the hazard.
Conclusion
We can agree arc welding safety is as important as learning how to weld. If you ignore the safety measures and precautions you increase a risk of serious injuries or even death. You should take the potential welding hazards seriously, and make sure you are well protected and aware of dangers. If you follow the guidelines, you minimize the chances of getting an arc eye, metal fume fever, or causing explosions and risking the life of your co-workers.
Resources:
- Arc Welding Safety, by National AG Safety Agency
- Occupational Safety and Health Standards – Welding, by OSHA – Occupational Safety and Health Administration
- Potential Welding Safety Hazards to Avoid, by OHS – Occupational Health and Safety
- Health, Safety and Accident Prevention, by TWI
- Arc Welding Safety Guide, by Lincoln Electric
- Welding – Overview and Type of Hazards, by CCOHS – Canadian Centre of Occupational Health and Safety
- Safety Glasses Standards, by ANSI/ISEA – American National Standards Institutes