MIG welding is a popular welding technique used for a wide range of metals, including steel, aluminum, and stainless steel. However, when it comes to welding copper, the process can be quite challenging.
Copper has unique properties that require special techniques to weld effectively. In this article, we will explore the intricacies of MIG welding copper.

From preparing the metal to choosing the right arc welding methods, equipment, and techniques, let’s dive in and discover how to MIG weld copper like a pro.
Why Is Copper Challenging To Weld?
Welding copper and copper alloys presents several unique challenges that require special techniques to overcome. Copper has very high thermal conductivity and electrical conductivity, which means it conducts heat very well. This makes it challenging to focus the heat on the welding area, and also results in rapid heat dissipation, making it difficult to achieve a stable weld pool.
Additionally, copper is highly susceptible to oxidation, meaning it easily forms a layer of oxide on its surface when exposed to air. This oxide layer can interfere with the welding process, causing porosity and other defects in the weld. Keep in mind that copper is a relatively soft metal, which means it can be deformed easily if too much force is applied during the welding process.
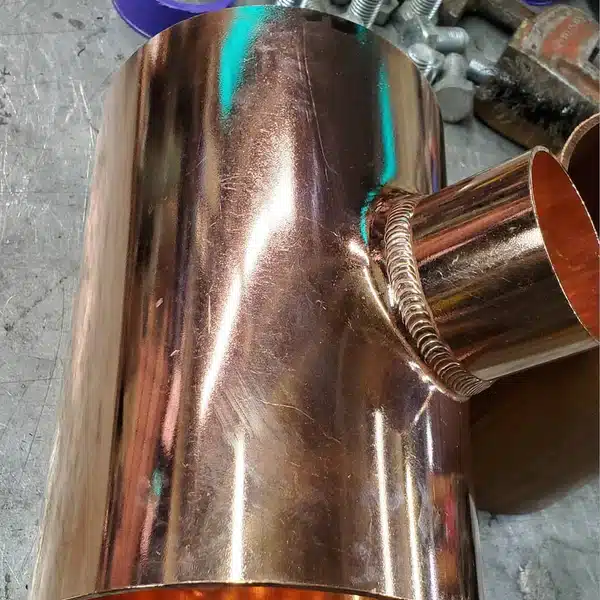

Copper Welding Methods
To successfully weld copper, it is important to choose the right welding method and equipment. Some of the preferred methods for welding copper include:
- TIG welding: Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (TIG) welding copper is often the preferred method. TIG welding uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode and a shielding gas to protect the welding area from oxidation. TIG welding provides precise control over the heat input and allows the welder to maintain a stable weld pool.
- Laser welding: Laser welding is another preferred method for welding copper. It uses a high-energy laser beam to melt the metal and create a weld. Laser welding provides excellent control over the heat input and can produce high-quality, precise welds. An alternative is a plasma arc welding process.
- Gas metal arc welding (GMAW): Gas metal arc welding, also known as MIG welding, can also be used to weld copper. However, it requires specialized equipment and techniques to overcome the challenges posed by copper’s high thermal conductivity and susceptibility to oxidation. The same thing applies to Shielded Metal Arc Welding.
How To MIG Weld Copper – Overview
Joining copper will require some special measures to overcome the unique challenges it presents. Start by preparing the copper surface by cleaning it with a wire brush or sandpaper to remove dirt, grease, or the oxide layer that could interfere with the welding process.
Next, choose the appropriate welding wire with high silicon content to prevent porosity and ensure good weld quality. Adjust your MIG welder settings, including wire feed speed, voltage, and amperage, based on the thickness of the copper you are welding.
Shield the welding area by using a shielding gas like argon or helium to prevent oxidation and porosity. When ready, start welding by directing the weld pool towards the center of the joint and moving the weld gun in a circular motion. Be cautious not to apply too much force, as copper is soft and can easily deform.
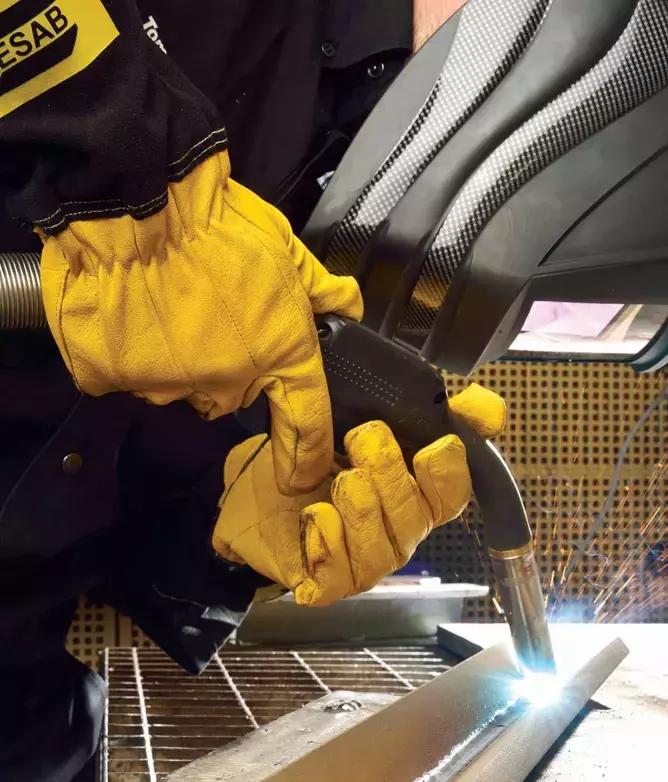

Monitor the weld carefully, adjusting settings as needed to maintain a stable weld pool. Once completed, allow the copper to cool slowly to avoid cracking. With these steps and proper techniques, you can MIG weld copper effectively and produce high-quality welds.
Preparing Copper Surface
The first step in preparing the copper surface is to clean it thoroughly. Use a stainless steel wire brush to remove any dirt, grease, or debris from the surface of the copper. This will ensure that the welding wire adheres to the surface properly and prevent any contaminants from being trapped in the weld. Additionally, copper is highly susceptible to oxidation, which can interfere with the welding process and cause porosity in the weld, so brush will also help you remove the oxide layer.
Degrease the surface of the copper to remove any oils or other contaminants that may be present. Use a degreasing agent or solvent to clean the surface thoroughly. Finally, use a clean cloth or paper towel to wipe down the surface of the copper and remove any remaining residue. Make sure the surface is completely dry before starting the welding process.
Choose The Right MIG Wire
The most suitable MIG filler metal for welding pure copper together is a wire with a high silicon content, typically referred to as silicon-bronze welding wire. Using a high-silicon wire can help prevent porosity in the weld. The silicon content in the wire reacts with the copper to form a silicon-copper alloy, which helps to improve the fluidity of the weld pool and prevent gas pockets from forming. It is similar to copper-nickel alloys and copper-zinc alloys.
The copper-silicon wire helps to maintain proper heat transfer, ensuring that the weld pool remains fluid and the weld is strong. The high silicon content in the wire provides excellent wetting characteristics, ensuring that the weld penetrates the base metal correctly and forms a strong bond.
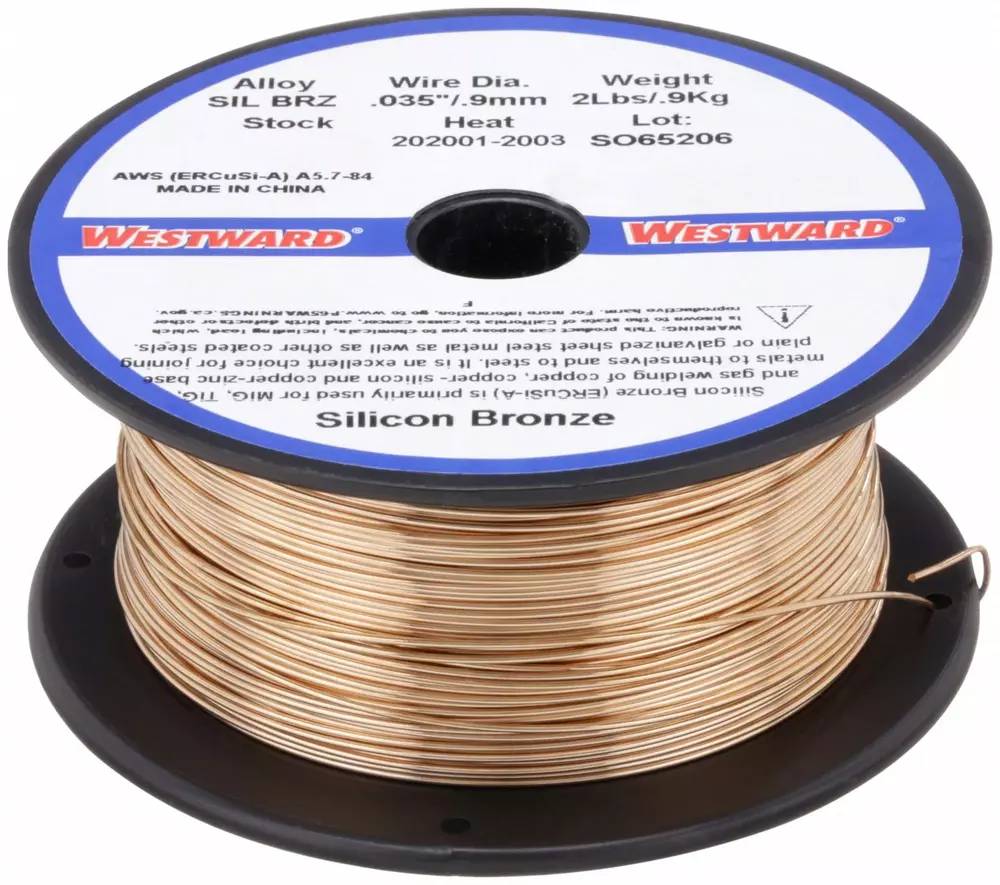

Deoxidized copper wire is another type of welding wire that can be used for MIG welding copper. The composition of this filler wire or electrode is copper 98% or more, manganese 0.1%, aluminum 0.1%, silicon 0.1%, iron 0.2%, lead 0.02%, and other metals are zinc, nickel, tin, and phosphorous. This results in a cleaner, more uniform weld and can help to reduce porosity. However, it’s important to note that deoxidized copper wire is typically more expensive than pure copper and silicon welding wire and may not be necessary for all welding applications.
Preheating The Copper Prior To MIG Welding
Preheating the copper can help to ensure that the weld penetrates the base metal correctly and forms a strong bond. This can result in higher quality, more durable welds. Copper is a good conductor of heat, which means that it can dissipate heat quickly. Preheating the copper can help to reduce the temperature gradient between the weld and the surrounding metal. Copper is prone to cracking, particularly when welded in thicker sections. Preheating can help to reduce the risk of cracking by reducing the thermal stress on the weld and the surrounding metal.

The appropriate preheat temperature for copper can vary depending on the thickness of the material and the specific welding application. Preheat the welding area of the copper workpieces to a temperature of 50º F to 750º F.
Shielding Gas Choice
The right shielding gas for MIG welding copper is typically a mixture of argon and helium. Argon is the primary shielding gas used for MIG welding copper, as it provides excellent coverage and protection against oxidation during the welding process.
Helium is often added to the argon to improve heat transfer and increase the fluidity of the weld pool. Helium has a higher thermal conductivity than argon, which can help to distribute heat more evenly and prevent overheating of the weld.

Generally, a ratio of 75% argon to 25% helium is suitable for most welding applications. However, thicker sections of copper may require a higher helium content to improve heat transfer and prevent overheating.
MIG Welder Features And Settings
There are a few special features that a MIG welding machine should have to weld copper successfully. Copper is a highly conductive metal, which means that it requires a high amperage output to weld effectively. Look for a MIG welding machine with a high amperage output, typically around 200 amps or higher, to ensure that it can handle the demands of the copper welding process.
Pulse welding can be beneficial for copper welding because it helps to control heat input and reduce the risk of overheating the material. Look for a MIG welding machine that has pulse welding capability or adjustable settings for controlling the welding current. A high-quality wire feeder is important for ensuring a steady, consistent flow of the welding wire during the welding process.
Welding Technique For MIG Welding Copper
When MIG welding copper weld metal, it’s important to use a steady, even motion to avoid overheating the material or causing weld defects. Move the welding gun in a straight line, keeping a consistent distance between the tip of the gun and the workpiece.
Use pulse welding or other techniques to control heat input and prevent overheating. Start welding by directing the weld pool towards the center of the joint and moving the weld gun in a circular motion. Be cautious not to apply too much force, as copper is soft and can easily deform.
For MIG welding copper, it’s recommended to maintain a stick-out of about 3/8 to 1/2 inch to ensure a consistent flow of welding wire. A slow travel speed can lead to excessive heat input and weld defects, while a fast travel speed can result in incomplete fusion.

Find a suitable travel speed for the specific welding application to achieve a high-quality weld. Keep an eye on the size and shape of the weld pool to ensure that it’s consistent and free from defects. Monitor the weld carefully, adjusting settings as needed to maintain a stable weld pool.
Cooling Down Copper
Cooling down copper after MIG welding is essential for several reasons. Copper is a highly conductive metal, which means that it can quickly dissipate heat and become hot during welding. Rapid cooling of hot copper can cause it to warp or distort, which can lead to problems with the finished product. Allowing the copper to cool down gradually reduces the risk of warping or distortion and helps to ensure that the final product is straight and true.
Allowing the copper to cool down gradually reduces the risk of these defects and helps to ensure a high-quality weld. This can improve the overall quality of the weld. This can lead to a stronger, more durable finished product.
Conclusion
MIG welding copper can be a challenging task, but with the right preparation, equipment, and technique, it is possible to achieve high-quality results with arc welding processes. Proper surface preparation, use of the appropriate wire and shielding gas, preheating, and careful control of heat input and travel speed are key factors in successfully welding copper.
It is also important to allow the copper to cool down gradually after welding to prevent warping, distortion, and other defects. By following these guidelines and practicing on scrap pieces of copper, welders can achieve strong, durable welds in their copper welding projects regardless of the process.
Resources
- https://homedistiller.org/forum/viewtopic.php?t=21819
- https://www.twi-global.com/technical-knowledge/job-knowledge/welding-of-copper-and-its-alloys-part-1-111
- https://workshopinsider.com/weld-copper/
- https://blog.dahlstromrollform.com/welding-copper-interior-framing
- https://yeswelder.com/blogs/yeswelder/how-to-weld-copper-mig-tig-and-stick-welding-copper-overview