MIG welding is a very useful and popular process among welders. It allows for a versatile finished weld and can be used in a variety of ways.
Some of its usages include working on low-allow steel, mild steel, and other alloy materials.

However, a shielding gas needs to be employed to prevent the contamination of the weld pool.
Welders usually use two types of shielding gases – carbon dioxide (100% CO2) or a binary 75% argon and 25% CO2 mixture. Both of them have their advantages and favorable usages. But a lot of people still ask themselves which one is better to use?
In this article, we will concentrate on the usage of 100% CO2 shielding gas and its advantages.
Why Chose a 100% CO2 Shielding Gas
The main question here is what things a welder needs to take into account before deciding on a MIG welding gas. If you are in two minds between pure CO2 and an Argon CO2 mix, there are a few things that will ultimately help you decide between the two.
You should analyze:
- The operating cost – Companies tend to cut costs when it comes to shielding gases and can do so by using CO2 instead of pure Argon or an Argon mix.
- Overall appeal and impact on productivity – Using CO2 shielding gases has a globular arc transfer with bigger droplet size. This results in a harsher arc and more spatter.
- Weld quality – An Argon CO2 mixture tends to keep the weld puddle more fluid which allows for easier work on the puddle and wet in the bead at the toes of the weld.
1. Low Price
Probably the main reason why welders use CO2 gas (also referred to as C100 gas) as their MIG welding gas is its cost-effectiveness. Welders see it as the best all-around gas MIG welding blend for mild steel.
Compared to the Argon and CO2 mixture (mostly referred to as C25), which is sold by the cubic foot, pure CO2 can be bought by the pound.

One can usually acquire it in liquid form, under pressure, with each pound yielding 8,741 cubic feet of gas.
The Argon CO2 mixture is about 4.5 times more expensive to obtain as opposed to CO2 MIG welding gas.
2. Portability
CO2 shielding gas takes the advantage when it comes to portability. Even though it can be packed in the same canister sizes as other gases, CO2 is more portable with smaller tanks. They even take things to extreme levels as there are 20 lbs tanks, usually used for paintball guns.
Unfortunately, you can’t weld all day using a small canister like this one. You will be sacrificing a bit on operating time but will be able to keep your gear as compact as possible.

3. Easier Refill
Basically, if you are using 5 lbs CO2 tanks, you can dispense 2 to 4 kegs before needing a refill. The best thing about straight CO2 is that is easily acquirable and that you can stop for a refill at your local welding supply store.
Additional places include homebrew shops, fire extinguisher companies, and aquarium supply stores.

4. Performance And Weld Pool Fluidity
Both Carbon Dioxide and Argon is an inert gas. However, CO2 becomes such only at low temperatures. At greater heat, Carbon Dioxide becomes reactive and acts stronger than Argon gas. This can have both good and bad sides.
First and foremost CO2 MIG welding gas has better joint weld penetration which grants smaller machines the ability to work on thicker metal.
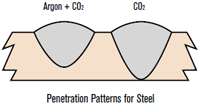
Next is that it allows for greater welding speed setting or gun travel. Finally, it offers far greater cleaning action and can even cut through rust and mill scale.
Equipment Required to MIG Weld With 100% CO2
In order to achieve the best results, you have to have the proper equipment at hand. The effort of choosing a correct shielding gas will be wasted if the equipment you have isn’t picking up the pace.
The main things to consider when choosing your equipment when working with pure carbon dioxide welding gas are the correct CO2 gas, a good MIG welder, a proper welding gas regulator, and the necessary MIG consumables.

1. Carbon dioxide CO2 Welding Gas
One or two canisters should be enough. There isn’t any significant difference between industrial-grade gas (99.5%) or food-grade gas (99.9%), so make your pick based on the price or general convenience.
2. MAG/MIG Welder
This should be called MAG welding (Metal Active Gas welding) but you don’t have to overthink this one too much as any proper gas MIG/MAG welding machine will do. However, MIG welders with more adjustments will work better. You can adjust your optimum settings when using carbon dioxide shielding gas and enhance your weld properties.
CO2 is less forgiving without Argon and has a smaller sweet spot. You can achieve better results and arc stability by adjusting the voltage and the wire feed speed.
3. Proper Welding Gas Regulator
Choosing the correct welding gas CO2 regulator is paramount. When you search for one make sure that it is adjustable for flow (CFH) and set by pressure (PSI).
You can use an Argon gas regulator, but only if it is rated to do so as not all Argon regulators are capable of running Carbon Dioxide. Under certain conditions, CO2 can frost and freeze a gas regulator. This can happen because of various work conditions, workplace temperature, high humidity levels, and high flow rates.
CO2 Tank Adapter
You can’t attach your carbon dioxide canister without a proper adapter. Welding regulators and cylinders use CGA-580 fittings while CO2 ones use a CGA-580 one. You can mount a CGA-320 to CGA-580 adapter and achieve proper productivity rates. A good piece of advice is to use a nylon washer seal to prevent leaks and freezing.
4. Welding Consumables
Luckily, all standard MIG welding consumables can be used with Carbon Dioxide shielding gas. However, increased oxygen created from CO2 can lead to porosity. So it is better to search for a MIG welding wire with powerful deoxidizers. Additionally, you can also run a dual-shielded process.
Getting the Shielding Gas to the Weld Pool
The main MIG gun consumables, namely the diffuser, the contact tip, and the nozzle, play a vital role in protecting the weld pool. A narrow nozzle, or if the nozzle gets clogged with spatter might result in supplying too little shielding gas to the weld pool.
When choosing MIG welding consumables, choose the elements that don’t allow spatter build-up and provide proper shielding gas application.
Characteristics of MIG Welding With 100% CO2
The main thing to know is that pure CO2 can change from a metal inert gas to a reactive gas in high temperatures. This will result in a better bite as opposed to Argon.
It will ultimately allow you to weld thicker materials at a faster travel speed and grant you the ability to cut through rust. Unfortunately, it also means that metal will be hard to weld. It will increase your travel speed and make welding thinner materials more difficult.
Arc Characteristics
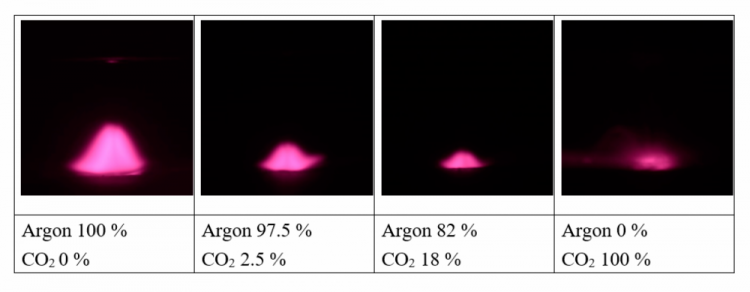
The biggest disadvantage of CO2 MIG welding is poor welding arc quality.
If we add carbon dioxide in small increments (5% to 25%) to Argon gas, it will add to arc stability. Pure carbon dioxide results in a rough and inconsistent arc with more spatter. You will be able to find a sweet spot but the arc will only be a bit more fickle.
The spray transfer process is not possible with CO2. You can also expect a short-circuit transfer at low currents or perhaps a globular transfer at high currents. But don’t sweat because cheaper non-professional MIG welding machines cant perform spray transfer or short-circuit transfer so you will have no problem there
MIG Welder Settings for 100% CO2
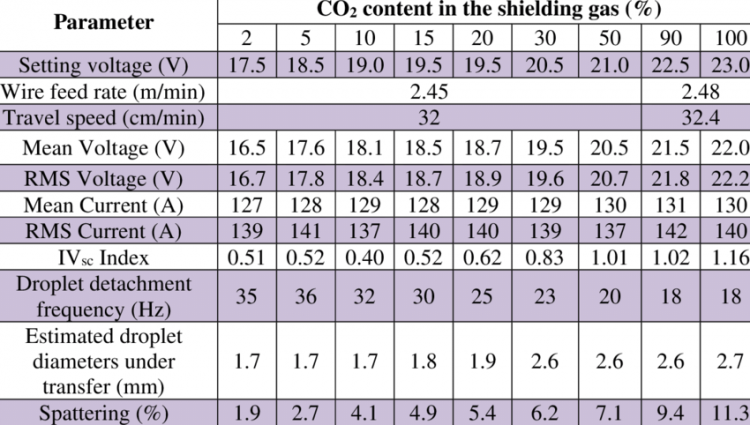
Every manufacturer will supply their machine with a gas recommendation guide. But in general, you will be needing more voltage. You will need to spend more time fine-tuning your machine to get it just right.
You will want to tinker a bit with inductance control or slope control which helps in setting down the arc. A low inductance setting is good for thin sheet metal. But for MIG welding with CO2 on thicker materials, a higher inductance setting is needed.
Weld Bead Appearance
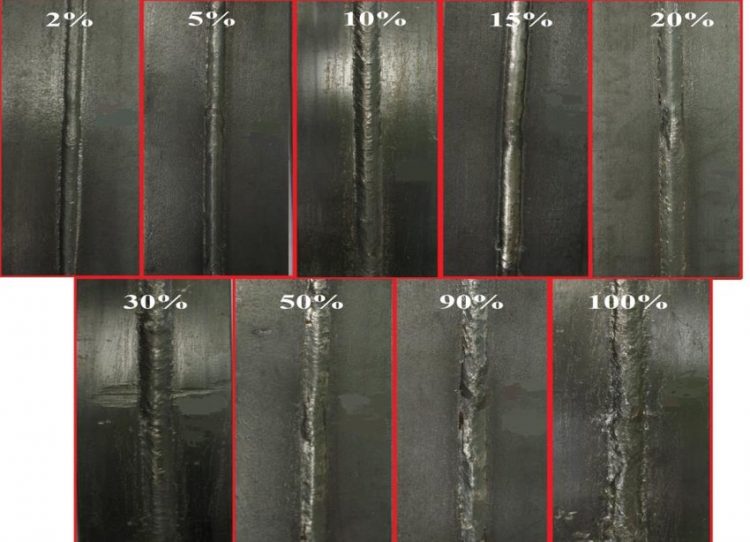
A weld bead profile usually gets wider with deeper penetration. This might be good when working on thicker metals but will be harder to control when welding auto body panels or other thin materials. You may resolve this by increasing gun travel speed and reduce penetration but will reduce welding time as well.
Frequently Asked Questions
When do you change a CO2 tank?
It is best to employ a double gauge regulator as that way you will know exactly how much carbon dioxide is left in the tank. Without it, it is going to be a bit of a guessing game.
How can CO2 freeze the regulator?
CO2 has a tendency to freeze a regulator due to the working conditions, temperature, high humidity, and high flow rate.
Does CO2 mess up MIG welds by adding carbon?
CO2 can cause more spatter to appear during the welding process, but you can clean the weld later on.
Conclusion
As you can see, pure CO2 is considered a good MIG welding gas that comes with various features and advantages. You can work on stainless steel, carbon steel, or various kinds of metal. However, it is more preferable to use it for thicker materials as opposed to thinner ones. Since it does come with its downsides, the more you are able to control them the better you will be able to use the positive aspects of its usage.
Sources:
- Applied MIG welding with 100% CO2, by Welding Tips and Tricks,
- Characteristics of Argon CO2 mixtures and pure CO2 shielding gases, by Lincoln electrics,
- MIG welder settings for 100% CO2, by Hobart Welder’s forum,
- Influence of CO2 content in shielding gas on the temperature of the Shielding Gas Nozzle, by Martin Lohse of Institute of Production Engineering
- Influence of CO2 content on operational performance, by Americo Scotti at Research gate.