When it comes to welding, the choice of shielding gas can make all the difference. MIG welding with a mixture of argon and carbon dioxide, commonly known as C25, has become a popular choice for welding enthusiasts and professionals alike.
The combination of these two gases provides the perfect balance of heat and penetration, making it an ideal choice for welding a wide range of materials.

In this article, we’ll delve into the science behind MIG welding with argon co2 mix and explore its benefits and limitations.
Role of Shielding Gases In MIG Welding
Shielding gas in MIG welding is used to protect the molten weld pool from atmospheric contamination that can cause defects or weaken the weld. The shielding gas is typically delivered to the weld through a nozzle that surrounds the electrode wire.
Argon and carbon dioxide are two common gases used in MIG welding, either separately or in combination.
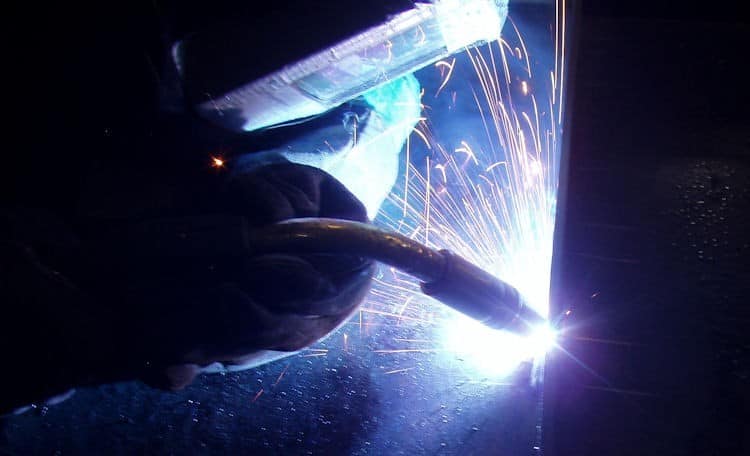

When combined in the right proportions, typically 75% argon and 25% carbon dioxide, the resulting gas mixture provides a good balance of heat and penetration, making it suitable for welding a variety of materials, including mild steel, stainless steel, and aluminum.
Pure Argon Inert Gas In MIG Welding
Pure argon MIG welding gas is usually used in the welding of non-ferrous metals such as aluminum, magnesium, and copper alloys. It provides excellent coverage and stability for the weld, producing a clean, smooth weld with minimal spatter.
One of the major advantages of using pure argon in MIG welding is its ability to produce a very stable arc, which results in better control over the weld pool and a cleaner finished weld. Additionally, it reduces the risk of porosity in the weld, which can weaken the joint. Pure argon is also less reactive than other gases, making it less likely to cause oxidation of the base metal, particularly when welding aluminum.
However, there are some drawbacks to using pure argon in MIG welding. It produces a lower heat output compared to other gas mixtures, which can limit its use in welding thicker materials. Additionally, pure argon is typically more expensive than other gas mixtures, which can increase the overall cost of welding.
Pure CO2 In MIG Welding
Pure carbon dioxide (CO2) MIG welding gas is commonly used as a shielding gas in MIG welding of mild steel due to its ability to produce a deeply penetrating arc. It provides a higher heat output than other gas mixtures, making it ideal for welding thicker materials.
One of the major advantages of using pure CO2 in MIG welding is its affordability. It is typically less expensive than other gas mixtures, making it a popular choice for budget-conscious welders. Additionally, pure CO2 is readily available and easy to use.
However, there are some drawbacks to using pure CO2 in MIG welding. It produces a more erratic arc compared to other gas mixtures, which can make it more difficult to control the weld pool and produce a clean finish. Pure CO2 is also more reactive than other gases, which can cause oxidation of the base metal and lead to porosity in the weld.
Why And When Do Welders MIX Argon and CO2 When MIG Welding?
Welders mix argon and carbon dioxide (CO2) when MIG welding to create a shielding gas that provides the best of both worlds in terms of weld quality and efficiency in welding mild steel. Argon is a noble gas that provides excellent coverage and stability for the weld, while carbon dioxide produces a more powerful arc and deeper penetration into the base metal.
When combined in the right proportions, typically 75% argon and 25% carbon dioxide, the resulting gas mixture provides a good balance of heat and penetration, making it suitable for welding a variety of materials, including mild steel, stainless steel, and aluminum.
One of the main advantages of using a mixture of argon and CO2 in MIG welding is the improved weld quality.
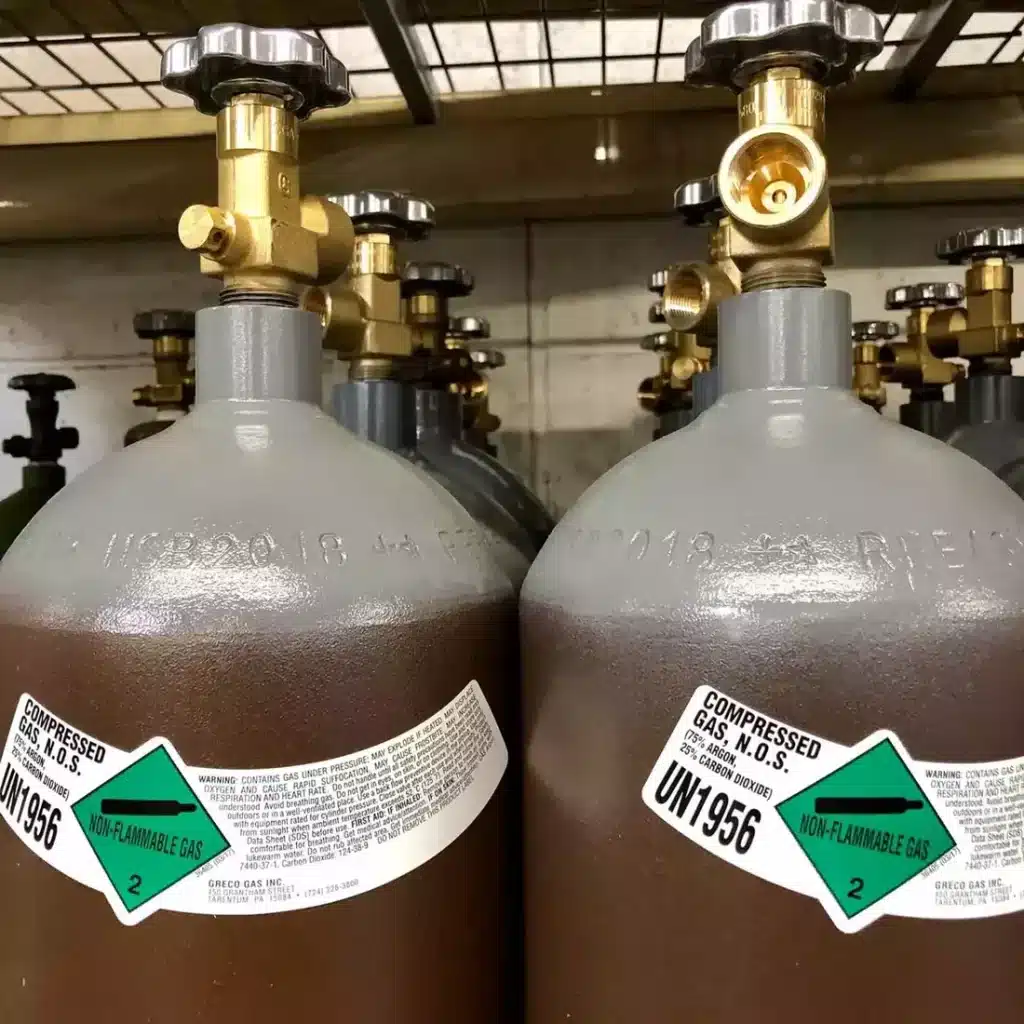

The combination of these two gases produces a smoother, cleaner weld with minimal spatter and porosity. This results in a stronger, more durable weld that is less likely to fail or weaken over time. The mixture also allows for better control over the weld pool, making it easier to produce high-quality welds with minimal defects.
In addition to improving weld quality, using a mixture of argon and CO2 can also increase efficiency and productivity. The mixture produces a higher heat output than pure argon, allowing for faster welding speeds (spray transfer) and better penetration into thicker materials. This can reduce the overall welding time and increase throughput, making it a more cost-effective option for large-scale welding projects.
Arc Properties Of MIG Welding With 75/25 Mix Of Argon and CO2
The C25 gas mixture produces a stable arc with good control and penetration, making it ideal for welding mild and low-alloy steels. The mixture’s combination of argon and CO2 gases provides a balance between coverage and arc intensity, allowing for better control over the welding process. The CO2 gas in the mixture provides a higher heat output, resulting in better penetration and faster welding speeds, while the argon gas provides better coverage and stability for the weld pool, resulting in a cleaner and smoother weld.
When MIG welding with C25 gas, the weld characteristics are improved due to the mixture’s ability to reduce spatter and produce a smooth, clean weld. The combination of argon and CO2 gases in the mixture reduces the risk of porosity in the weld, which can weaken the joint. Additionally, C25 gas can reduce the formation of slag and spatter, which can make post-weld cleanup easier.
Another advantage of using C25 gas in MIG welding is that it is a versatile gas mixture that can be used on a variety of thicknesses and types of mild steel. The mixture’s higher heat output allows for welding thicker materials with better penetration, while its argon content provides good coverage and stability, making it ideal for welding thin materials as well.

Can You MIG Weld Aluminum With 75/25 Argon/Co2?
MIG welding aluminum with a mixture of 75% argon and 25% carbon dioxide is generally not recommended. This is because aluminum is a highly conductive material, and the CO2 gas in the C25 mixture tends to produce a more aggressive arc that can cause burn-through or warping on the thin and highly conductive aluminum. Additionally, an oxide layer that forms on top of the aluminum welds has a lower melting point, so it can reach the weld, causing defects and imperfections.
For welding aluminum, it is recommended to use a pure argon gas or an argon-helium gas mixture, which can provide the necessary coverage and heat for successful aluminum welding. The pure argon gas provides better coverage and stability for the weld puddle, while the argon-helium gas mixture provides better heat transfer and penetration into the base metal.
Can You MIG Weld Stainless Steel With C25?
MIG welding stainless steel with 75% argon and 25% carbon dioxide is generally not recommended. This is primarily due to the potential issues associated with the oxide layer that forms on stainless steel during welding.
Stainless steel naturally forms a thin oxide layer on its surface, which provides corrosion resistance. However, when welding stainless steel, this oxide layer must be properly managed to ensure a strong, clean weld.
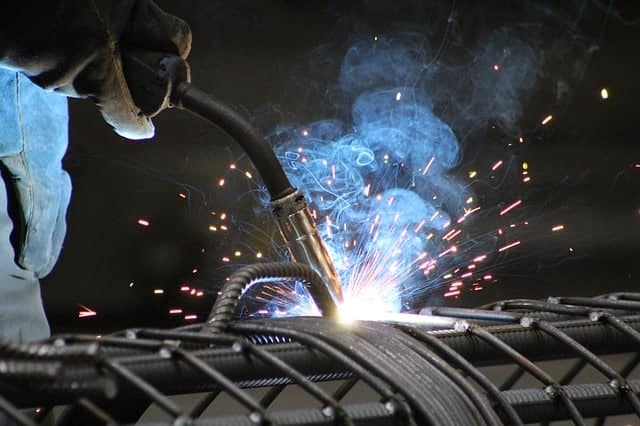

The C25 gas mixture contains carbon dioxide, which is active gas that can react with chromium in stainless steel and lead to the formation of chromium carbides. This can result in a reduction of corrosion resistance and compromise the weld’s integrity.
To prevent this issue and ensure high-quality welds on stainless steel, you should use a gas mixture that is specifically formulated for stainless steel welding. Typically, a mixture of pure argon or an argon-helium gas mix, or argon/oxygen gas blend is preferred.
Is It Better To Weld Steel With Pure CO2 or C25?
Whether it’s better to MIG weld steel with pure CO2 or C25 gas mixture depends on the specific welding application and the type of steel being welded.
Pure CO2 gas is often used in heavy-duty welding applications where higher penetration and heat output is required. It is also a more cost-effective option than the C25 gas mixture. However, pure CO2 gas can produce a more erratic arc and more spatter, which may require more post-weld cleanup. Additionally, pure CO2 gas can be challenging to use when welding thin materials, as it can result in burn-through or warping due to the higher heat output.
On the other hand, a C25 gas mixture (75% argon and 25% CO2) is a more versatile option that provides better coverage and stability for the weld pool. The mixture also produces a more stable arc, which can result in a cleaner and smoother weld. The CO2 gas in the mixture provides better penetration and heat output than pure argon, making it a better option for thicker materials. Additionally, the argon gas in the mixture provides better coverage and stability for welding thin materials.
Can You Use Argon/Carbon Dioxide Shielding Gas Mixture In TIG Welding?
TIG welding requires strictly inert shielding gas coverage for best results, so you shouldn’t use Argon CO2 mix. Semi-inert gases such as CO2, or reactive gas such as Oxygen or Nitrogen can interfere with the tungsten electrode, causing contamination and tungsten inclusion, weakening the weld.
TIG welding is all about high weld quality, so you don’t want to save on shielding gas as you can do with your MIG welder. High skills requirements, higher equipment cost, and slower speeds of TIG are one of the reasons many novice welders prefer MIG welding in the first place.
Pros And Cons Of MIG Welding With C25 MIG Gas Mix
Pros:
- C25 gas mixture produces a stable arc with good control and penetration, making it ideal for welding mild and low-alloy steels.
- The combination of argon and CO2 gases in the mixture provides a balance between coverage and arc intensity, allowing for better control over the welding process.
- C25 gas reduces the risk of porosity in the weld, which can weaken the joint.
- The higher heat output of the CO2 gas in the mixture allows for better penetration and faster welding speeds.
- The argon gas in the mixture provides better coverage and arc stability for the weld pool, resulting in a cleaner and smoother weld.
- C25 gas is versatile and can be used on a variety of thicknesses and types of mild steel.
Cons:
- C25 gas mixture is not recommended for welding aluminum or other non-ferrous metals.
- The CO2 gas in the mixture can produce more spatter than other gas mixtures, which can require additional post-weld cleanup.
- The C25 gas mixture may not provide enough heat for the successful welding of thicker materials or materials that require higher welding temperatures.
- C25 gas mixture can be more expensive than pure CO2 gas, which can be a consideration for some welders.
Conclusion
MIG welding with a C25 gas mixture (75% argon and 25% carbon dioxide) offers several advantages and considerations. The mixture provides a stable arc with good control and penetration, making it well-suited for welding mild and low-alloy steels. The combination of argon and CO2 gases in the mixture strikes a balance between coverage and arc intensity, resulting in cleaner, smoother welds with reduced porosity, and that’s why MIG welders across the globe prefer it.
However, it’s important to note that C25 gas is not recommended for welding aluminum or non-ferrous metals with your welding machine. The potential for increased spatter and the need for post-weld cleanup should also be considered.
Resources
- https://www.millerwelds.com/resources/article-library/what-gas-should-you-use-for-mig-welding-in-diy-applications
- https://eurekaoxygencompany.com/2019/10/30/welding-mild-steel/
- https://bbs.homeshopmachinist.net/forum/general/13779-why-c25-gas-for-mig#post297210
- https://www.weldingtipsandtricks.com/can-75-argon-25co2-be-used-to-weld-stainless-steel-.html
- https://weldingweb.com/vbb/threads/534881-Mig-welding-stainless-with-C25