Shipbuilding and marine applications demand the highest level of precision, durability, and safety. In this context, welding is a crucial aspect of the construction process.
Among various welding methods, Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) welding is widely used due to its mechanical properties and its ability to produce high-quality, defect-free welds with exceptional strength and aesthetic appeal.

TIG welding is an ideal choice for shipbuilding and marine applications where the welds must withstand harsh environments, such as saltwater corrosion, high pressure, and extreme temperatures.
In this article, we will explore the benefits of TIG welding in shipbuilding and marine applications, as well as its limitations and best practices for achieving optimal results.
Introduction Of Welding In Shipbuilding And Marine Applications
Welding has been used in the shipbuilding industry and marine applications for over a century, with the earliest recorded use dating back to the late 1800s. However, the welding techniques used in those early days were not as advanced as today’s methods.
The introduction of electric arc welding in the early 20th century was a game-changer for shipbuilding and marine applications. The first ship to be built entirely using electric arc welding (shielded metal arc welding) was the American tanker, “S.S. Carolinian,” in 1924.
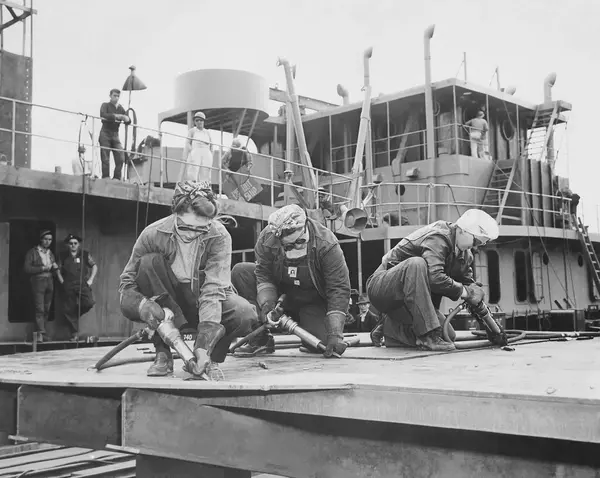

This was a significant milestone in the history of shipbuilding as manual metal arc welding (stick welding) it demonstrated the viability of welding as a construction method for large ships. Subsequently, the use of welding in shipbuilding and marine applications grew rapidly, and by the 1930s, it had become the primary method of joining steel plates and sections.
Over the years, welding technology has continued to evolve, and today, shipbuilders use a range of advanced welding techniques such as gas tungsten arc welding, gas-shielded arc welding, submerged arc welding, oxyacetylene welding, plasma arc welding, and flux-cored arc welding, among others. These techniques have enabled shipbuilders to construct stronger, more durable, and safer vessels that can withstand the harsh marine environment.
The Role Of TIG Welding In Shipbuilding And Marine Applications
Tungsten Inert Gas welding is a popular welding technique used in shipbuilding and marine applications. It is a versatile and precise method that provides several advantages over other welding techniques.
The role of TIG welding in shipbuilding and marine applications is to create high-quality, defect-free welds that can withstand the harsh marine environment.
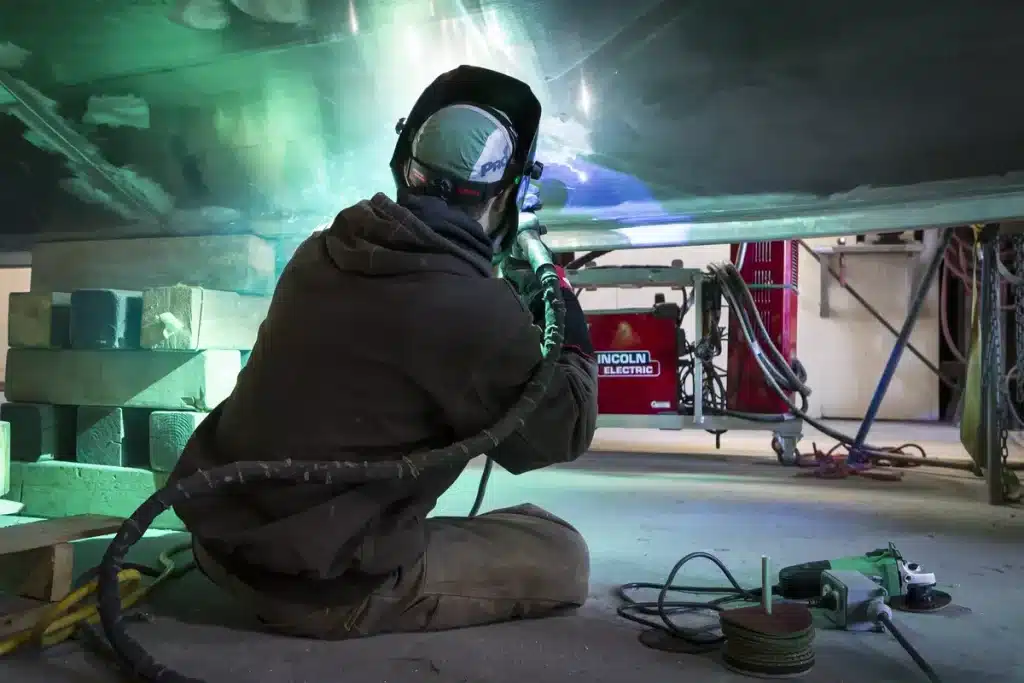

TIG welding produces high-quality welds with low heat input and a narrow, concentrated arc, which allows for precise control of the weld pool and welded joints. This results in high-quality, aesthetically pleasing welds that require minimal post-weld cleanup.
One of the main advantages of TIG welding in shipbuilding and marine applications is its ability to produce welds that are highly resistant to corrosion. This is because TIG welding produces a shielded environment that prevents atmospheric contamination of the weld pool. Additionally, TIG welding produces a weld bead that is uniform in size, shape, and composition, which reduces the likelihood of stress corrosion cracking.
Another advantage of TIG welding in shipbuilding and marine applications is its ability to weld thin materials with minimal distortion. TIG welding produces a low heat input, which minimizes heat distortion in the weld joint surrounding material. This is especially important when welding thin materials such as sheet metal or pipes, where distortion can lead to warping or buckling.
A career in TIG welding for shipbuilding and marine applications can be a rewarding and challenging choice. As shipbuilding and marine industries continue to grow, the demand for skilled TIG welders is also increasing. TIG welding is a specialized skill that requires extensive training and experience, but it can lead to a fulfilling career with many opportunities for advancement.
TIG Welding Career in Shipbuilding And Marine Applications
TIG welding careers in shipbuilding and marine applications typically start with completing a welding program at a vocational school or community college. Many employers also offer apprenticeships that provide on-the-job training and allow for hands-on experience in a shipyard or marine facility.
As TIG welders gain experience, they may advance to supervisory or management positions, such as a welding inspector or quality control manager.
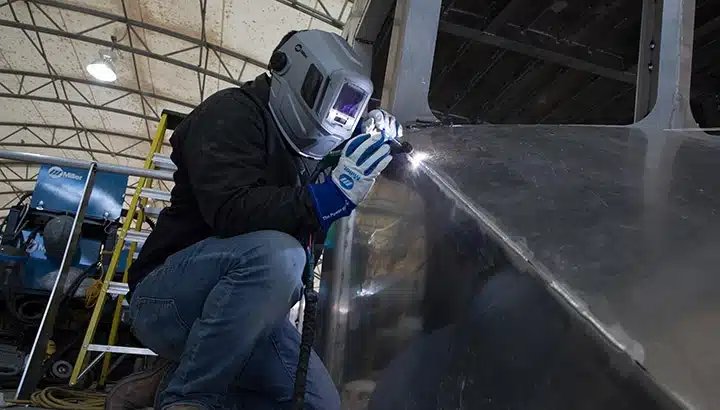

These roles involve overseeing the welding process and ensuring that all welds meet the required standards and specifications.
The benefits of a career in TIG welding for shipbuilding and marine applications include job security, competitive pay, and the opportunity to work on complex and challenging projects. TIG welders in shipbuilding and marine applications also play an essential role in ensuring the safety and durability of vessels that operate in harsh marine environments.
Challenges of TIG Welding In Shipbuilding And Marine Applications
While TIG welding is an excellent choice for weld metal for shipbuilding and marine applications, it also presents some challenges that welders and shipbuilders must overcome to achieve optimal results.
One of the main challenges of TIG welding in shipbuilding and marine applications is the need for a clean and dry welding environment. Any moisture or contaminants in the welding environment can negatively impact the quality of the weld and increase the risk of corrosion.
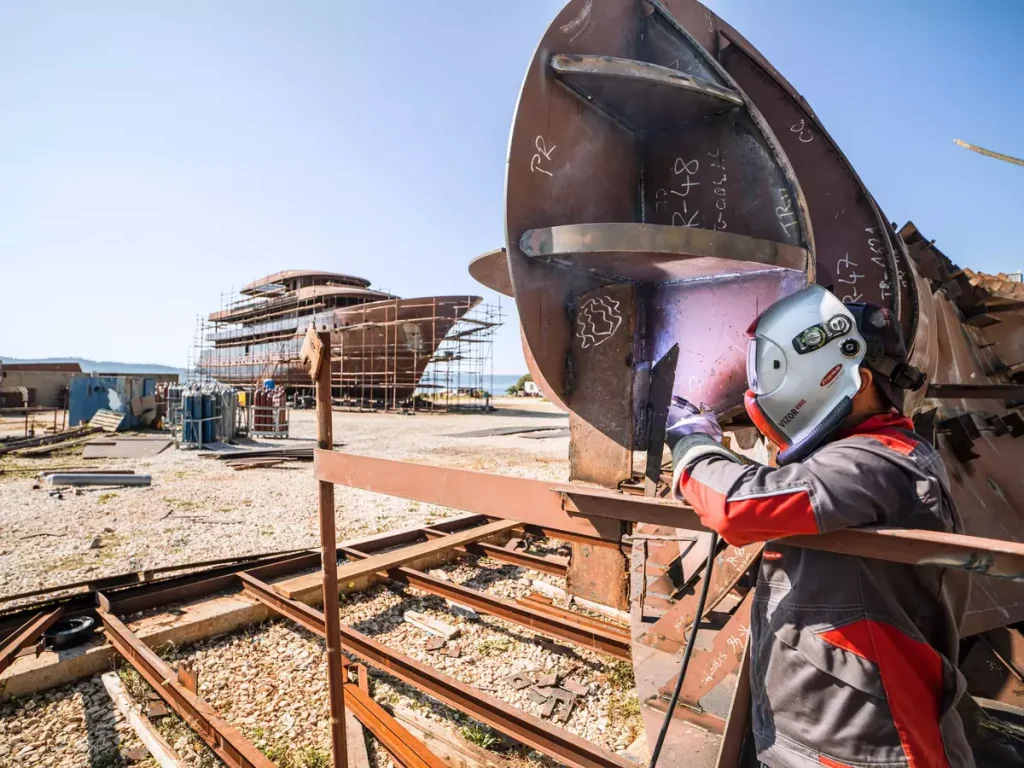

This requires careful preparation and maintenance of the welding area and the use of appropriate shielding gas and consumables. Another challenge of TIG welding in shipbuilding and marine applications is the limited speed of the process.
TIG welding produces a narrow and concentrated arc, which requires multiple passes to cover a large area. This can lead to longer welding times and increased labor costs, especially when welding thick materials or complex geometries.
The size and weight of the materials being welded can also pose a challenge for TIG welding in shipbuilding and marine applications. The process may require specialized equipment, such as overhead cranes or welding positioners, to maneuver the materials into the correct position for welding. Welders must also have the physical strength and dexterity to handle heavy and bulky materials.
Finally, TIG welding in shipbuilding and marine applications requires a high level of skill and experience. Welders must be able to accurately control the welding parameters, including the heat input, welding speed, and filler material and metal selection, to produce high-quality and defect-free welds. This requires extensive training, practice, and ongoing professional development.
Requirements and Responsibilities Of TIG Welders In Shipbuilding And Marine Applications
TIG welders play an important role in shipbuilding and marine applications, ensuring that the vessels are safe, durable, and capable of withstanding the harsh marine environment. To meet the requirements and responsibilities of this role, TIG welders must possess certain qualifications, skills, and knowledge.
Responsibilities:
- Interpretation of engineering drawings, blueprints, and specifications to determine the welding requirements for a given project.
- Preparation of welding surfaces by cleaning, grinding, and degreasing to ensure optimal welding conditions.
- Setting up and operating TIG welding equipment, including welding torches, power supply sources, and shielding gas systems.
- Controlling welding parameters, including heat input, welding speed, and filler metal selection, to produce high-quality, defect-free welds.
- Inspection of welds using visual inspection techniques and non-destructive testing (NDT) methods to ensure compliance with industry standards and specifications.
- Documentation of welding activities and quality control procedures to ensure traceability and compliance with regulatory requirements.
To start a TIG welding career in Shipbuilding and marine applications, you will need:
- Formal education and training in welding, typically through a vocational school or community college program.
- Certification in TIG welding from a recognized welding authority, such as the American Welding Society (AWS).
- Knowledge of welding processes, types of welding equipment, and welding materials commonly used in shipbuilding and marine applications.
- Understanding of welding safety practices, including personal protective equipment (PPE), electrical safety, and fire prevention.
Risks Of Welding In Shipbuilding And Marine Environments
Welding in shipbuilding and marine environments presents several potential risks to workers, equipment, and the environment. These risks include Fire and explosion hazards, Toxic fumes and gases, Electrical hazards, Noise exposure, Physical hazards, Corrosion and material degradation.
To mitigate these risks, workers must undergo proper training and use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), such as welding helmets, respirators, gloves, and protective clothing.

Employers must also implement proper ventilation systems, establish safety protocols, and provide regular maintenance and inspection of equipment and materials. Regular monitoring of air quality and noise levels can also help to identify and mitigate potential hazards.
Is TIG Welding Career In Shipbuilding And Marine Worth The Risk?
The decision to pursue a career in TIG welding in shipbuilding and marine applications depends on several factors, including an individual’s personal goals, interests, skills, and tolerance for risk.
While welding in shipbuilding and marine environments presents potential risks, many welders find the work rewarding and fulfilling. The work requires a high level of technical skill and expertise, and welders in this field often have the opportunity to work on complex and challenging projects. Additionally, shipbuilding and marine industries are important and vital to the global economy, and welders play a crucial role in ensuring the safety and durability of the vessels used in these industries.
That being said, it is important to recognize that the risks associated with welding in shipbuilding and marine environments can be significant and should not be taken lightly. Welders must undergo proper training and use appropriate safety measures to minimize potential hazards.
Ultimately, whether this career is worth the risk depends on an individual’s personal circumstances, goals, and risk tolerance. It is important to thoroughly research and understand the potential risks and rewards of a career in TIG welding in shipbuilding and marine applications before making a decision.
How Much Do TIG Welders In Shipbuilding And Marine Industry Make?
According to the U.S. Bureau Of Labor Statistics, TIG welders in ship and boat building can make an annual mean wage of $53,720, or $25.83 an hour. Shipbuilding and marine are one of the highest concentrated industries for welders, with 10.37% of all workers being welders. However, these are only the statistics, while things in practice can differ on state, experience, company, and work hours.
That’s why we see reports where entry-level TIG welders with 0-2 years in shipbuilding and marine make approximately $30,000 a year. In the lowest paying states, this number for apprentices can drop to $26,100 a year, or over $12.54 an hour. Meanwhile, seasoned welders with more than 7 years of experience can easily make up to $100,000 or even more. Yet again, this differs on the state and company, so most wages differ between $60,000-80,000 a year.
Conclusion
TIG welding, with MIG welding (Gas metal arc welding, Metal Inert Gas welding) and Stick/Arc welding process, plays a critical role in shipbuilding and marine applications, ensuring the safety, durability, and functionality of vessels that operate in harsh marine environments. While welding in these environments presents potential risks, welders who undergo proper training and use appropriate safety measures can mitigate these hazards and perform their duties effectively.
Welding in shipbuilding and marine applications requires a high level of technical skill, expertise, and attention to detail, making it a challenging but rewarding career for those who are willing to take on the associated risks. Ultimately, whether this career is worth the risk depends on an individual’s personal circumstances, goals, and risk tolerance.
Resources
- http://kgmarinefabrication.com/blogs/advantages-of-tig-welding-for-marine-applications/
- http://www.ijmerr.com/uploadfile/2015/0409/20150409110634573.pdf
- https://www.sunbeltrentals.com/resources/blog/industrial-tool/tig-welding-applications/
- https://www.secindustrial.com/blog/types-of-welding-used-in-the-shipbuilding-industry/
- https://www.marineinsight.com/naval-architecture/common-welding-methods-weld-defects-shipbuilding-industry/