TIG welding is a popular method of joining metal parts that requires high precision and skill. However, as with any welding process, it can be hazardous if proper safety measures are not taken.
TIG welding machines, in particular, require careful handling due to the high voltage and current involved. Accidents can result in severe electrical shocks, burns, and even death.

Therefore, it’s critical to understand the potential risks and take necessary precautions to ensure TIG welding machine safety.
In this article, we’ll delve into the essential safety measures that you need to follow when using a TIG welding machine, and how they can help protect you and your colleagues from harm.
Why Is Safety Crucial In Welding?
Welding is a process that involves joining metals using high heat and an electric arc, making it inherently dangerous if proper safety precautions are not taken. Welding poses a range of safety hazards, including electrical shock, burns, eye damage from radiation, toxic fumes and shielding gas poisoning, and fire or explosion risks.
Employers and workers in the welding industry must prioritize safety to prevent accidents and injuries that could have severe consequences, including permanent disability, loss of limbs, or even death.
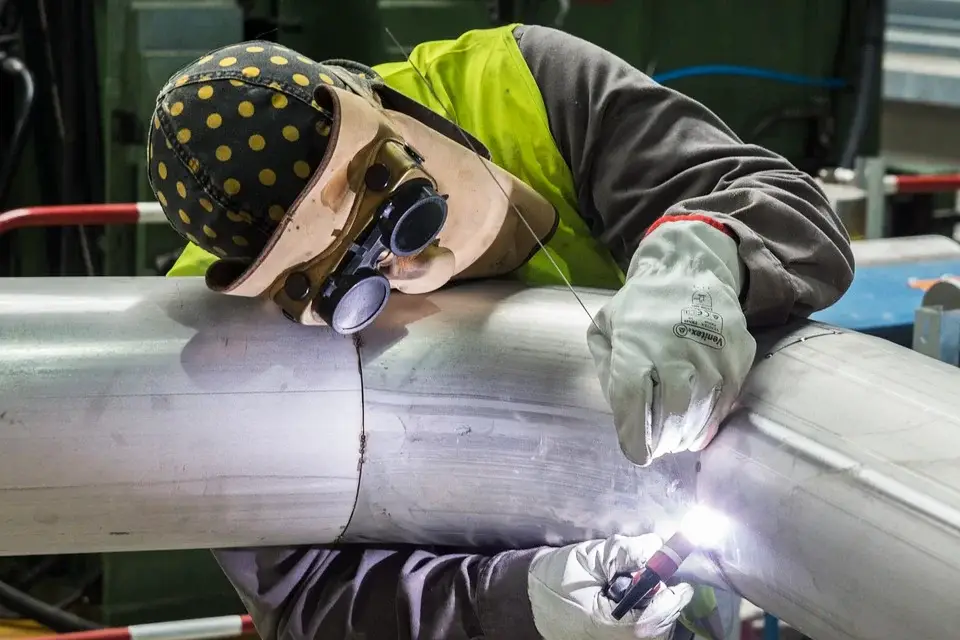

Ensuring proper safety measures, such as wearing protective clothing, using ventilation systems, and following proper welding procedures, can reduce the risks associated with welding and create a safer work environment.
Additionally, safety measures can help prevent damage to equipment, minimize the risk of property damage, and reduce costs associated with insurance, lost workdays, and medical expenses. In summary, safety is crucial during welding to protect workers’ health and well-being, prevent accidents, and ensure a productive and efficient workplace.
Is TIG Welding Safe, And What Are Potential Hazards?
TIG welding (Tungsten inert gas), also known as Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW), is a welding process that uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode to heat and melt the metal, which is then fused together with a filler metal or material. While TIG welding produces high-quality welds, it poses a range of safety hazards that must be carefully managed to prevent accidents and injuries. Commonly, these hazards include the risk of electric shock, intense heat, toxic fumes, fire and explosion, and risk of injuries.
Electrical Shock In TIG
One of the most significant hazards associated with TIG welding is electrical shock. TIG welding machines (welding power source) use high voltage and amperage, which can result in severe shocks if safety precautions are not followed.
Welding operators must use appropriate safety equipment, such as gloves, boots, and helmets, to protect themselves from electrical shock.

Electric shock can occur in several ways during TIG welding. One common cause primary voltage shock is direct contact with the welding electrode, which is usually made of tungsten and remains in contact with the metal being welded. If the electrode comes into contact with the worker, it can result in an electrical shock.
Another cause of electrical shock is indirect contact with the welding current. This can occur if the worker touches a conductive material, such as a metal structure, that is part of the electrical circuit. In this case, the worker becomes part of the electrical circuit and can receive a shock.
The welding operator can also receive an electrical shock if the welding machine is not properly grounded and if welding cables are damaged. If the machine is not grounded, the electrical current can flow through the metal parts of the welding equipment, including the welding table, creating an electrical hazard.
To prevent electrical shock in TIG welding, it is essential to follow proper safety procedures, such as grounding the welding machine correctly, wearing appropriate protective equipment, and turning off the machine when not in use. Employers must also provide proper training and ensure that workers are familiar with the hazards associated with TIG welding and know how to avoid them. Regular inspections of equipment and wiring can also help to identify and prevent electrical hazards before they become a serious risk.
Intense Heat
Another hazard is the intense heat generated during the TIG welding process, which can cause burns to the skin and eyes. You must wear appropriate personal protective equipment, including heat-resistant gloves, clothing, and a welding helmet with a protective lens shade to prevent exposure to the arc flash.
TIG welding can also produce toxic fumes and gases, such inert gases such as ozone, nitrogen oxides, and metal fumes, which can be harmful if inhaled.
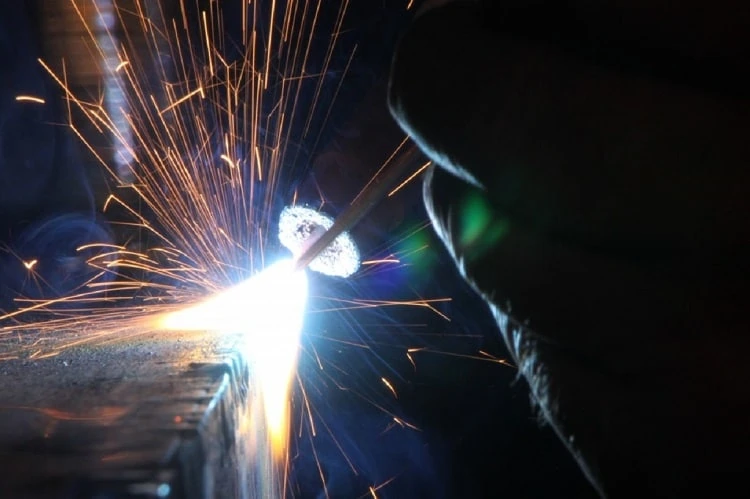

Proper ventilation systems must be in place to remove these hazardous substances from the work area and ensure that workers are not exposed to them.
Skin burns can occur if the worker comes into contact with the hot metal or the welding torch. Welders must wear appropriate personal protective equipment, such as heat-resistant gloves and clothing, to do hot work and protect themselves from burns.
Even though TIG welding is carried out at lower amps than Stick or MIG, the heat really shouldn’t be disregarded. You can wear thinner protective clothes to get more dexterity and enough protection, but the risk is always present. To prevent the hazards associated with intense heat during TIG welding, you must follow proper precautions and safety procedures, such as wearing appropriate personal protective equipment, including heat-resistant gloves, clothing, and welding helmets with protective lens shades.
Physical Injuries And Ergonomic Hazards in TIG Welding
In addition, TIG welding requires a steady hand and precise control, making it more challenging to perform in awkward positions or cramped spaces. This can lead to ergonomic hazards, such as repetitive strain injuries, back pain, and muscle strains.
One common ergonomic hazard in TIG welding is repetitive strain injuries (RSI).
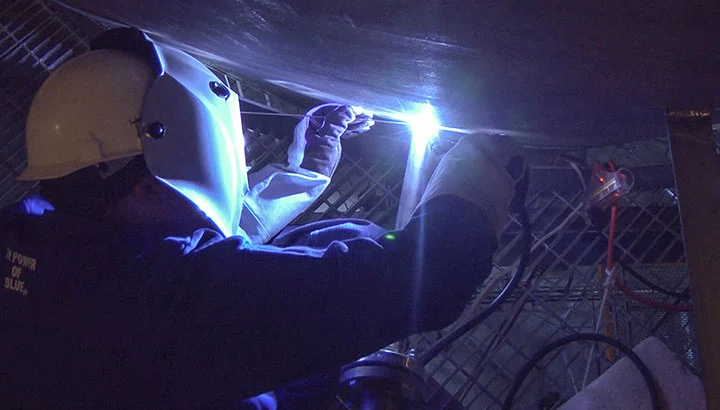

Welders must maintain a steady hand while welding, which can lead to overuse injuries in the hands, wrists, and arms. These injuries can cause pain, inflammation, and reduced mobility, making it difficult for workers to perform their jobs.
Another ergonomic hazard is back pain, which can occur due to the prolonged standing and awkward body positions required during TIG welding. Workers must stand for long periods, often in awkward positions, which can lead to back strain and pain.
Muscle strains are also common in TIG welding due to the physical demands of the job. Welders must hold the welding torch in a specific position for extended periods, which can lead to muscle strains in the neck, shoulders, and arms.
To prevent ergonomic hazards and injuries in TIG welding, you must follow proper safety procedures, such as taking regular breaks, using ergonomic equipment, and maintaining proper posture. Employers can also provide training on safe work practices and equipment, such as adjustable welding tables and chairs, to reduce the risk of injury.
Risk of Fire And Explosions
TIG welding poses fire and explosion risks due to the use of flammable gases and liquids, such as oxygen and acetylene, and the possibility of sparks and hot metal form welding arc particles igniting nearby materials.
Workers must follow proper welding procedures, store and handle flammable materials safely, and have fire extinguishers readily available.

One common cause of fire during TIG welding is the ignition of flammable materials, such as paper, wet clothing,, or other combustible substances. Welders must ensure that the welding area is clear of any flammable materials and that they have a fire extinguisher readily available in case of a fire.
Explosions can occur if the welding process takes place in a confined space or if there is a buildup of combustible gases in the welding area. These gases can be produced during the welding process or may be present in the surrounding environment. Welders must ensure that the area is well-ventilated and that combustible gases are properly monitored and controlled.
To prevent fire and explosion hazards in TIG welding, you must follow proper safety procedures, such as keeping the welding area clear of flammable materials, monitoring and controlling combustible gases, and wearing appropriate personal protective equipment. You must also have a fire extinguisher readily available and be trained in its proper use.
Toxic Fumes During TIG Welding
Welding produces fumes and gases that can be hazardous to the health of the welder and others in the surrounding area.
The fumes and gases produced during welding can come from several sources, including the welding material, the welding rod or wire, and the surface being welded. The fumes contain particles and gases, including metal oxides, nitrogen oxides, carbon monoxide, and ozone, which can be harmful if inhaled.

The amount and type of fumes produced depend on the welding process, the type of material being welded, and the welding conditions. For example, TIG welding typically produces lower levels of fumes compared to other welding processes, such as MIG welding. Also, shielding gas, such as carbon dioxide or inert gas, can cause severe poisoning when welding in a confined space.
The inhalation of welding gases can cause several health problems, including respiratory irritation, metal fume fever, and long-term lung damage. That’s why you must take appropriate measures to protect yourself from welding fume, such as wearing respiratory protection, using local exhaust ventilation to remove fumes from the breathing zone, and maintaining a safe distance from the welding area.
Exposure to UV/IR Radiation
TIG welding can pose a significant risk of exposure to UV (ultraviolet) and IR (infrared) radiation, which can be harmful to the skin and eyes. Welding produces intense light and heat that can emit UV and IR radiation, which can cause immediate and long-term damage to unprotected skin and eyes.
Exposure to UV radiation can cause sunburn-like symptoms, including redness, itching, and blistering of the skin.

Prolonged exposure can also increase the risk of skin cancer. Welders must wear appropriate protective clothing, such as long-sleeved shirts, pants, and gloves, to protect their skin from UV radiation.
Exposure to IR radiation can cause severe eye damage, including burns to the cornea and retina, and even blindness. Welders must wear appropriate eye protection, such as welding helmets or goggles with appropriate filters, to protect their eyes from IR radiation.
You can avoid this issue by wearing protective, long-sleeved clothing and a proper TIG welding helmet. The auto-darkening function of the TIG welding helmet should support the low amp TIG starts.
How To Improve TIG Welding Machine Safety
Here are some tips on how to improve TIG welding safety:
- Wear appropriate personal protective equipment, including flame-resistant clothing safety shoes, gloves, eye protection, and respiratory protection.
- Ensure proper ventilation in the welding area to prevent the buildup of toxic fumes and gases.
- Keep the air in the welding area clear of flammable materials and combustible gases.
- Use proper grounding techniques to prevent electrical shock hazards.
- Check and maintain all welding equipment regularly to ensure proper function and safety.
- Follow proper welding techniques allied processes and procedures to prevent accidents and injuries.
- Use proper lifting and handling techniques when moving heavy metal objects or welding equipment.
- Train all workers working manual welding proper safety procedures and ensure they are aware of potential hazards.
- Maintain a clean and organized work area to prevent accidents and injuries.
- Have a first aid kit and fire extinguisher readily available in case of an emergency.
Conclusion
TIG welding is a highly skilled and precise welding process that can produce high-quality welds. However, it also poses a range of safety hazards that must be carefully managed to prevent accidents and injuries. Electric shock, burns, toxic fumes, ergonomic hazards, and fire and explosion risks are all potential hazards associated with TIG welding.
Employers and workers in the welding industry working with TIG welding processes must prioritize safety to create a safer work environment. This includes providing appropriate personal protective equipment, proper ventilation, and following safe welding procedures. Regular inspections and maintenance of equipment and wiring can also help to prevent electrical hazards and other safety issues.
Resources
- https://safetyculture.com/topics/welding-safety/10-welding-safety-rules/
- https://www.eng.uwo.ca/files/departments-units/student-shop/2018/sop-welder-tig.pdf
- https://www.co2meter.com/blogs/news/is-tig-welding-dangerous
- https://www.axxair.com/en/blog/tig-welding-in-complete-safety
- https://www.hse.gov.uk/welding/other-welding-risks.htm