Welding is a complex and skilled art, but it is far from impossible to master. TIG welding, in particular, is an especially intricate technique involving the use of a non-consumable tungsten electrode, filler rod, and argon-based shielding gas.
If you are a beginner or a welder looking to improve his TIG welding skills, then this article have you covered.

In this article, we will provide tips and tricks on how to successfully TIG weld, from proper equipment selection to best practices for welding techniques. By covering the steps outlined in our article, everyone can achieve good-looking TIG welds.
What Is TIG Welding & Why Is It Hard To Master?
How to TIG weld and what is GTAW Welding: TIG welding, also known as Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW), is a welding process that utilizes an arc between a non-consumable tungsten electrode and the workpiece to join two metals. It is considered the most challenging to master due to its more complicated setup and operation compared to other welding processes.
The tungsten electrode used in TIG welding must be carefully and precisely manipulated for the weld to be successful.

This process requires the welder to control the distance between the electrode and the workpiece as well as maintain a constant arc length. Additionally, the welder must keep track of the filler metal addition rate and use of shielding gas. All of these steps must be carefully monitored for a successful weld since any variation will lead to contamination of the weld pool, which can cause cracking, porosity, and other defects that can lead to failure.
Furthermore, TIG welding requires a high level of precision since it is often used on thin metals (e.g., aluminum or stainless steel) or in applications where high-quality welds are essential (e.g., aerospace or medical industries). As such, any error in the manipulation of the tungsten electrode can cause a variety of issues, so it is a less forgiving process compared to MIG welding, for example.
TIG Welding techniques: Walk the Cup vs Freehand
Walk The Cup TIG Welding technique
Walking the cup TIG welding is a technique used to weld thin sheet metal or to weld “faster”. It involves using a small, pointed tungsten electrode and walking it around the joint in an overlapping pattern while feeding filler material into the joint.
In the welding trade and among other welders, the “walk the cup” TIG welding technique is what separates a veteran welder from a beginner.
In most instances, using this technique in a welding test while applying for a job as a welder will most likely land you that position with the perk of a higher salary. In the welding trade and among other welders, the “walk the cup” TIG welding technique is what separates a veteran welder from a beginner. In most instances, using this technique in a welding test while applying for a job as a welder will most likely land you that position with the perk of a higher salary.
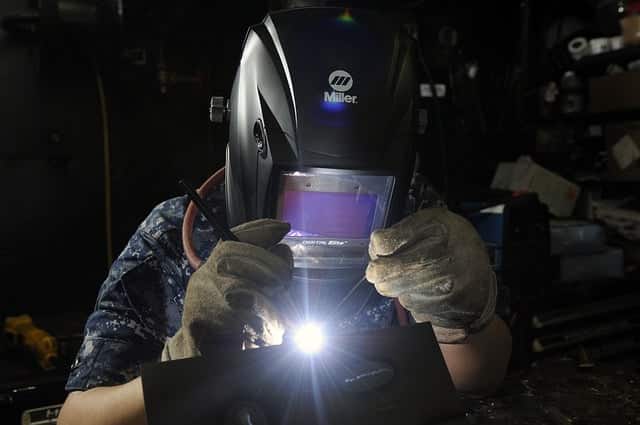
This technique produces high-quality welds faster and with minimal distortion due to its ability to create even heat distribution across the entire weld area. The process begins by optional preheating the workpiece to ensure that it is at the correct temperature for welding.
The tungsten electrode is held at an angle of approximately 10-15 degrees from the surface of the workpiece and moved in a circular motion along the circumference of the joint.
As it moves, filler material is added to fill any gaps between the pieces being joined. Additionally, this method allows for precise control over both heat input and travel speed, making it ideal for welding thin materials such as aluminum or stainless steel.

Proper control of these parameters ensures that there are no gaps or voids in the welded area, which can lead to weak spots or cracking over time.
What is the difference between walking the cup TIG and the freehand TIG welding technique?
There are three main differences, They are the speed of welding, the amount of heat, added material over a certain period of time, and the “looks” of a finished weld beat.
The walk-the-cup method is faster and somewhat easier to perform when you properly master it. Considering that you are moving the weld pool faster, you are adding less heat to the weld peace, and you prevent distortion.
Also, the finished weld looks much more appealing to the eye. It’s mainly used for pipe welding, especially on stainless steel where the finished weld can’t be too much tempered with.
On the other hand, freehand TIG welding does not require this type of movement; instead, it relies on controlling heat input and travel speed with one hand while manipulating filler material with the other. It’s the first technique you learn in a welding school and a technique that will be used mostly throughout your career because of its versatility.
TIG Weld Tips For successful welds
If you’re getting started with the TIG welding process as a hobby or as a potential new welding career that could pay off in the long run, it’s good to develop a clear plan for practicing your TIG welding techniques. The TIG process is specialized and has a narrow margin of error, so you can’t practice enough.
To learn TIG welding you will need a greater amount of skill than other welding processes due to its slow speed and tedious nature. This makes it more difficult for those who are inexperienced in welding to learn and perform effectively since there is no room for error when performing this process.
To get the best results with TIG welding, you should:
- Clean the pieces and work in a clean environment
- Get to know your welder and its settings
- Try to get comfortable
- Practice on the scrap metal
- Develop a consistent welding technique
- Choose the right equipment and consumables (filler rod)
Cleanliness Is Crucial With TIG Welding
Cleanliness is critical for successful TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding for a number of reasons.
Firstly, contaminants on the surface of the components being welded can cause porosity in the weld joint, leading to structural weakness and potential failure.
Contaminants can also cause undesirable oxides, which can lead to poor joint penetration and lack of fusion.
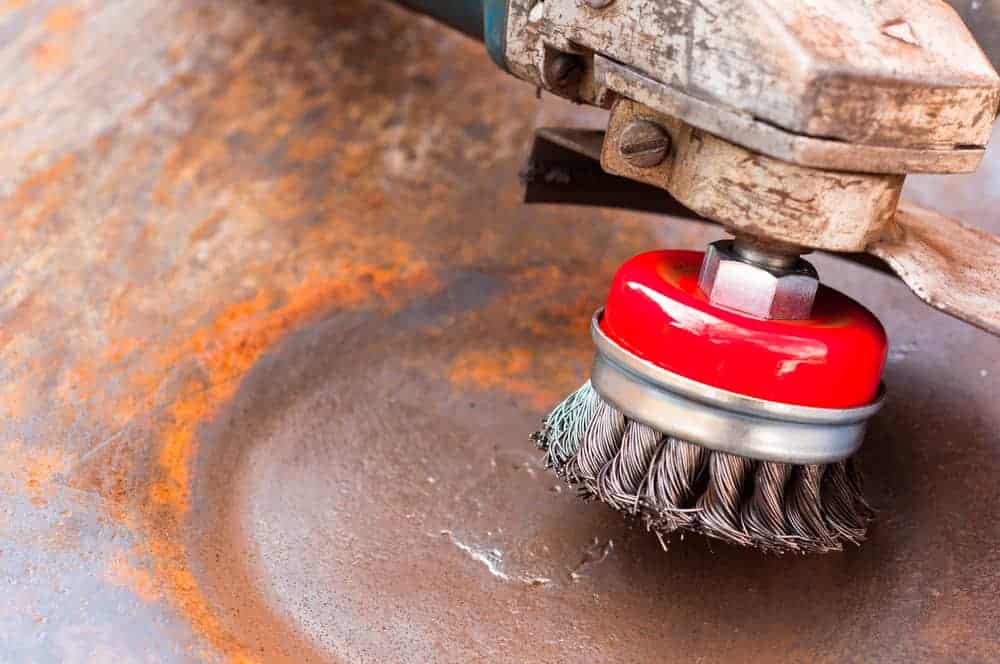

Secondly, contamination on the tungsten tip inside the welding torch can create an unstable arc and potentially lead to erratic arc starting and stopping. This can cause excessive spatter, which results in a rough weld surface finish. Finally, dirt and debris on the welding surface can also act as an insulator, preventing adequate heat transfer to the workpiece and thus resulting in poor-quality welds.
In order to ensure successful TIG welding, it is important to maintain a clean environment both before and during the welding process. Before beginning the weld, all surfaces should be wiped down with a clean cloth, wire brush or dampened with a solvent such as acetone or alcohol to remove any dust or contaminants from the material being welded.
During welding, it is important that the tungsten electrode is kept free from any contamination by frequently wiping it down with a non-contaminating cloth. Additionally, protective shielding gas should be used to ensure that no foreign particles enter the weld area during welding. Failure to properly maintain cleanliness during TIG welding can result in poor weld quality, poor strength characteristics of the weld joint reduced fatigue life of the components being joined, and even catastrophic failure of the finished product.
Get The Hang Of Your TIG Welder
TIG welding is a complex process that requires the operator to have an in-depth understanding of the machine, its settings and how these settings can be adjusted to produce optimal welds.
You must also have a sound knowledge of the material being welded, its properties, and the correct welding technique for it. Without this level of understanding, you can quickly run into issues that could result in failure.
One of the potential issues is that two TIG welding machines from different manufacturers, in some cases even from a single one, can perform differently with the same parameters and settings. That’s why you should always read and follow the manufacturer’s recommendations. Unfortunately, TIG welders can be one of the most complex machines on the market. With the vast number of available options, setting the TIG welder can feel like operating a spaceship for beginners.
To get the hang of your welder, you should start with simple and recommended settings. From there, you can work your way to see what fits you best. Don’t be afraid to use more advanced settings such as pulse, balance, upslope or downslope. Once you master using them, you can control the entire welding process, which is crucial when welding delicate metals.
Getting Comfortable
Getting comfortable when TIG welding is important because it helps ensure that the weld is safe and of a high quality. Proper positioning of the welder’s body, good posture, and a comfortable grip on the TIG welding torch will help to ensure that the weld has proper penetration, even distribution, and uniformity. This is especially true for difficult-to-weld metals such as aluminum, stainless steel, and nickel alloys. Luckily, most TIG welding is done indoors and in comfortable positions, which is not always the case with Stick pipeline welding.
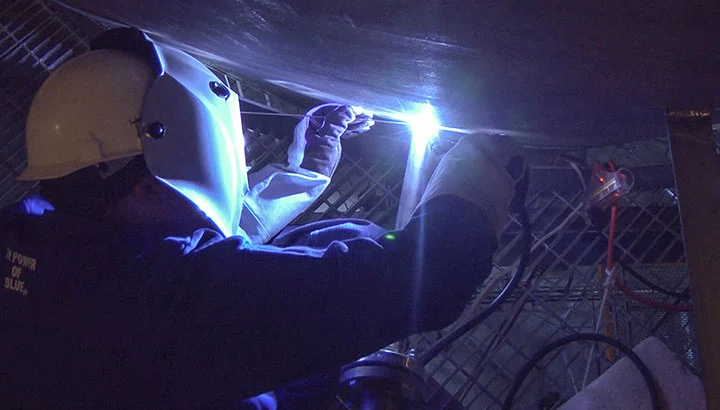

Poor posture can lead to fatigue which can cause inconsistent arc length and travel speed resulting in an inconsistent weld bead profile. In addition, you can experience issues such as poor bead appearance, lack of penetration, porosity or undercut in the weld metal, poor fusion at the joint edges, burn-through of the base metal, and inadequate fillet welds. That’s why you should always try to provide good support for your hands or arms is crucial for moving the torch with precise control.
Practice On Scrap Metal
Practicing TIG welding on scrap metal is an essential step to becoming a successful welder. It allows you to become more familiar with the process, develop your technique, and hone your skills in a safe and controlled environment.
To do so, use a scrap metal that is same type and thickness of your project. That way, you can learn to adjust settings that are appropriate for the material being used. For example, you can learn how to adjust the amperage and gas flow settings which are necessary for optimal heat input.
Additionally, practicing on scrap metal with Gas Tungsten Arc Welding helps welders develop overall manual dexterity since you will be manipulating the torch while keeping it at the correct angle and maintaining a steady hand speed. Furthermore, practicing TIG welding on scrap metal helps welders become familiar with the specific welding processes that they will use when working on actual projects. This includes learning how to start and stop welding properly as well as developing their arc stability and travel speed.
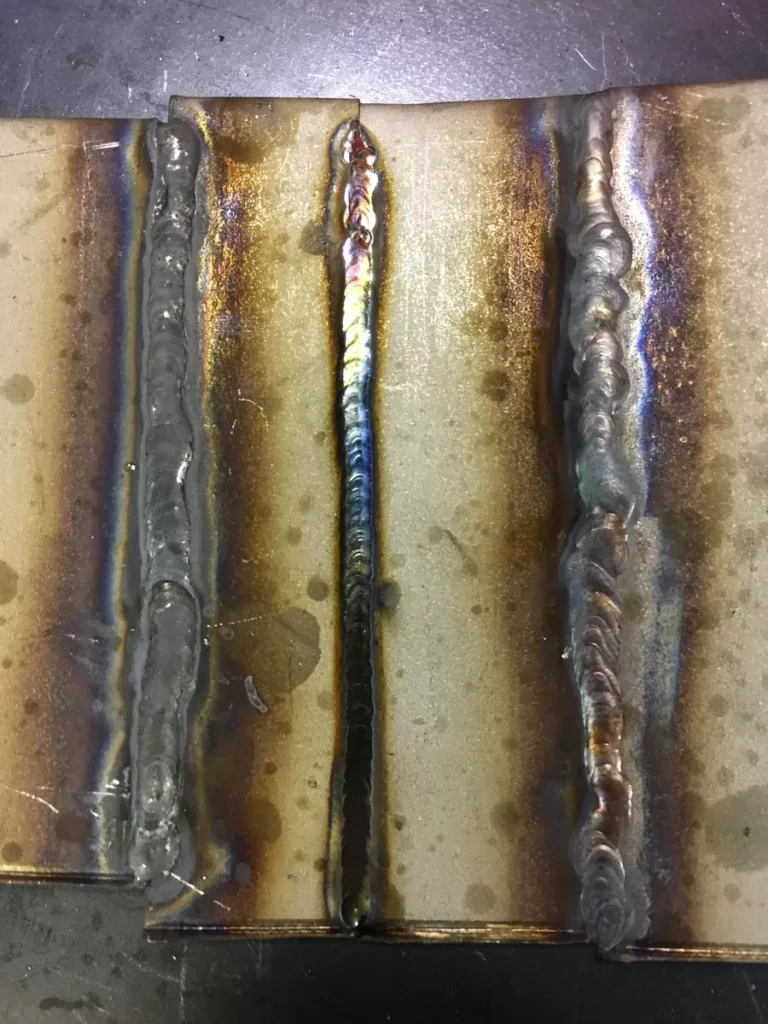

Consistency Is Crucial Wen Learning How To TIG Weld
Maintaining a consistent welding technique is essential for successful TIG welding. Here are some tips to help ensure that your welds are of the highest quality:
- Keep your torch angle consistent. Holding the torch at a constant angle while welding will help keep the arc centered in the joint and ensure consistent welds. It’s also important to maintain a constant distance from the joint to ensure proper penetration and avoid burning through the base material.
- Use a good welding rod. Using a quality filler material with the correct diameter for the type of metal being welded (e.g. welding aluminum or stainless steel) will help ensure that welds are of uniform size and strength. Micro TIG welding won’t need a filler wire, but you can start by
- Move the torch smoothly. Moving the torch smoothly, without jerking or shuddering, will help prevent “cold lapping” (unevenly distributed heat), which can lead to weak welds or cracking in certain metals.
- Use proper shielding gas at adequate flow rates. Using too much shielding gas can cause excessive spatter and porosity, while too little gas can lead to oxidation and poor penetration in the molten metal weld puddle. Therefore, use inert shielding gas and consult your welding manual to find the appropriate flow rate for different metals and thicknesses of material being welded.
- Monitor your amperage settings. The amperage setting determines how much heat is generated in a welding arc and should be adjusted depending on the material being welded, its thickness, and other factors such as joint geometry or environmental conditions like wind or drafts in a shop. Too much amperage can cause burn-through, while too little can result in cold laps or undercut in the weld bead.
- Use back purge when welding stainless steel or other materials prone to oxidation. The proper back purge will help protect materials prone to oxidation from forming an oxide layer on the base material which can weaken the bond between metal pieces being welded together or damage their protective coatings like paint or plating if any have been applied previously.
- Maintain uniform travel speed. Maintaining a uniform travel speed when welding helps ensure that each pass is of uniform depth and width, This prevents cold laps, porosity, burn-through, undercut, or other defects that can weaken welds or hinder their appearance.
Get The Right Equipment For The Job
Choosing the right welding equipment is essential when learning TIG welding, as it can significantly impact the quality of the weld and your safety throughout the process. The main components required for successful TIG welding are a welding machine, protective equipment, and consumables.
A TIG welder is used to generate an electric arc which will heat up the metal workpiece and facilitate welding.
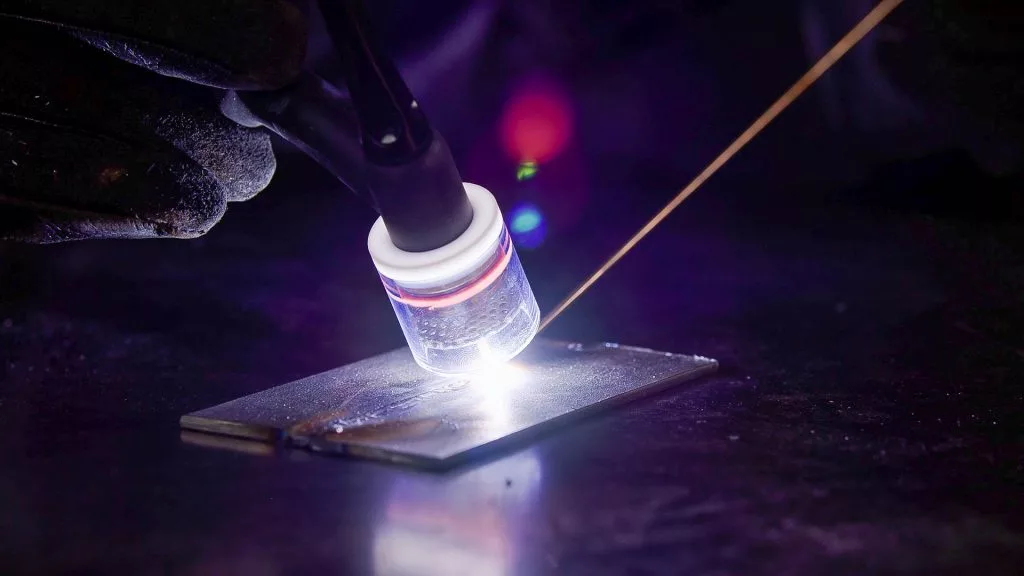

It is important to select a welder with the appropriate amperage rating for the job at hand in order to ensure that the arc is hot enough to properly fuse the metals together. If the amperage rating is too low, it can result in an incomplete weld or an underfilled weld. On the other hand, selecting a welder with too high of an amperage rating can lead to excessive heat buildup and potentially dangerous situations with spatter and sparks flying off. In addition, you can buy yourself a beginner TIG welder with basic functions, or an advanced machine with state-of-the-art features.
Protective equipment should also be worn while TIG welding in order to protect against burns, sparks, and ultraviolet radiation from the arc. This includes a welding helmet, gloves, fire-resistant clothing, and safety glasses. A proper fit is key when selecting welding gear, as ill-fitting apparel can reduce safety levels and make it difficult to perform quality welds.
Finally, consumables such as tungsten electrodes and filler rods should be chosen carefully as they are integral for producing a good weld. Tungsten electrodes come in different sizes and shapes depending on the application and need to be selected based on the material type being welded as well as the amperage rating of the welder being used. Filler rods should also be chosen according to material type with consideration given to its composition, tensile strength, ductility, and melting point.
Conclusion
Successful TIG welding requires the right tools, techniques, and experience. Following the tips outlined in this article will help ensure a successful weld.
Taking the time to learn the basics and practice regularly is essential to developing the skills needed for successful TIG welding. Even though it will take you more time than like with MIG (Metal Inert Gas) welding, with the right preparation and dedication, anyone can become an expert TIG welder.