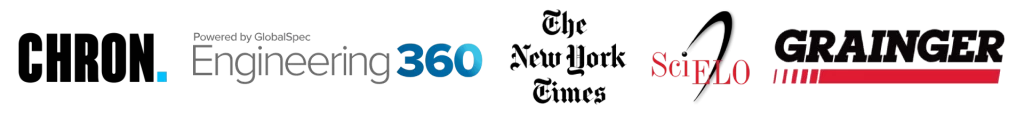Automated MIG welding, also known as Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW), has revolutionized the welding industry by integrating advanced technology and robotic systems into the welding process.
This innovative method utilizes a combination of electricity, shielding gas, and a consumable wire electrode to create high-quality and precise welds.
By automating the process, manufacturers can achieve faster production rates, improved consistency, and enhanced weld quality while reducing labor costs and minimizing human error. In this article, we will delve into the principles behind automated MIG welding, explore its benefits and applications across various industries, and discuss the key considerations for implementing this cutting-edge technology.
Applications And Reasons To Choose Automated MIG Welding
Automated MIG welding offers significant advantages and common applications in industries such as automotive manufacturing, aerospace, construction, and general metal fabrication. The technology enhances production rates, ensures consistent weld quality, reduces labor costs, and improves overall efficiency.
According to a study by the International Federation of Robotics, the automotive industry accounted for 33% of total robot installations in 2020.

Automated MIG welding enables automotive manufacturers to achieve high production rates and maintain consistent weld quality. For instance, Tesla utilizes automated MIG welding robots in their production line, enabling them to produce up to 7,000 electric vehicles per week with precise and efficient welds.
The construction industry is also experiencing the advantages of automated MIG welding. Large-scale construction projects, such as bridges and infrastructure, require consistent and high-quality welds to ensure durability and safety. Automated MIG welding systems offer improved efficiency and accuracy, enabling construction companies to complete projects faster and more cost-effectively.
Moreover, the benefits of automated MIG welding extend to the manufacturing of appliances, furniture, and other metal products. By automating the welding process, manufacturers can achieve faster production rates and reduce labor costs.
Advantages Of MIG welding automation
Automated MIG welding provides several advantages over manual welding methods:
Increased productivity: Automated MIG welding significantly improves productivity by reducing cycle times and increasing welding speeds. Robots can work continuously without the need for breaks, resulting in higher production rates and shorter project completion times.
Consistent weld quality: The welding robot performs welds with consistent precision, eliminating human errors and variations in technique. This ensures uniformity in weld quality, leading to stronger and more reliable welds. Consistency is particularly crucial in industries like aerospace and automotive, where weld integrity is critical for safety.
Cost savings: Although the initial investment in automated MIG welding equipment may be higher, the long-term cost savings of automated welding system are substantial. Robots can operate 24/7, reducing labor costs and eliminating the need for overtime payments. Additionally, automated systems minimize material waste, as they can precisely control the amount of filler metal used, resulting in cost-efficient welding processes.
Improved safety: By automating the welding process, companies can enhance worker safety by reducing exposure to hazardous environments. Robots can operate in challenging conditions, such as high temperatures or confined spaces, without risking human health. This not only reduces the risk of accidents and injuries but also promotes a safer work environment overall.
Enhanced weld accuracy: Robotic automation utilize advanced sensors and feedback mechanisms to ensure precise weld placement. This accuracy is especially beneficial when working with complex or intricate weld patterns, enabling manufacturers to meet strict design specifications consistently.
Flexibility and versatility: Automated MIG welding systems offer flexibility in handling a wide range of materials and components. They can be easily programmed to adapt to different welding applications, making them suitable for various industries and product types. This versatility allows manufacturers to streamline their operations and accommodate changing production needs.
Documentation and traceability: Automated MIG welding systems often include data logging and reporting features. These capabilities enable manufacturers to track and document welding parameters, such as voltage, current, and travel speed. The collected data provides valuable insights for process optimization, quality control, and compliance with industry standards and regulations.
Parts Of Automated MIG System
An automated MIG welding system typically consists of several key components that work together to facilitate the welding process. The most important parts of MIG automated systems are:
- Welding power source
- Wire feeder
- Welding torch
- Robotic arm or positioner
- Sensor system
- Control system
- Shielding gas
These are the main components of an automated MIG welding system. However, depending on the specific application and complexity of the system, additional components like wire cleaning devices, wire straighteners, and cooling systems may be included to further enhance the welding process and system performance.
Automated MIG Power Source
The automated MIG power supply plays a crucial role in providing the necessary electrical energy for the welding process. It offers control over voltage or current output, and advanced features such as waveform control, synergic control, and digital interfaces enhance the efficiency, precision, and user-friendliness of the automated MIG welding system.
The power source typically operates on either alternating current (AC) or direct current (DC).
DC power sources are commonly used in automated MIG welding due to their ability to provide a stable and consistent arc. They can be further categorized as either constant voltage (CV) or constant current (CC) power sources.
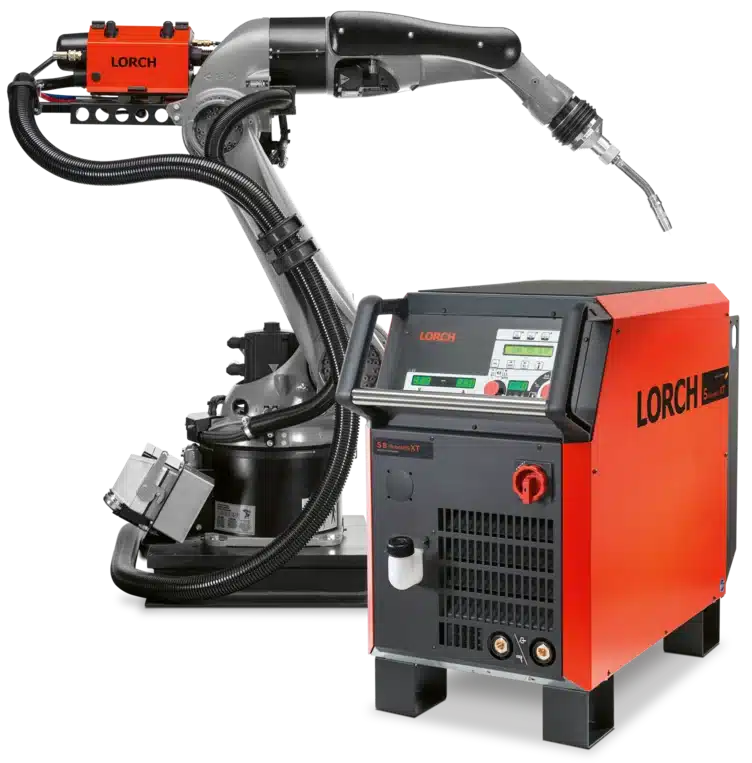

Wire Feeder In Automated System
The wire feeder in an automated MIG welding system uses a motorized feed mechanism, wire drive rolls, tensioning mechanisms, and wire guide tubes to provide a continuous and controlled feed of the consumable wire electrode to the welding torch. The wire feeder’s functionality is crucial in continuously feeding wire and accuracy, which contributes to the quality and efficiency of the MIG welding process.
The wire feeder typically holds a spool of the consumable wire electrode. The wire is wound onto the spool, and it is available in various diameters and materials depending on the welding application.
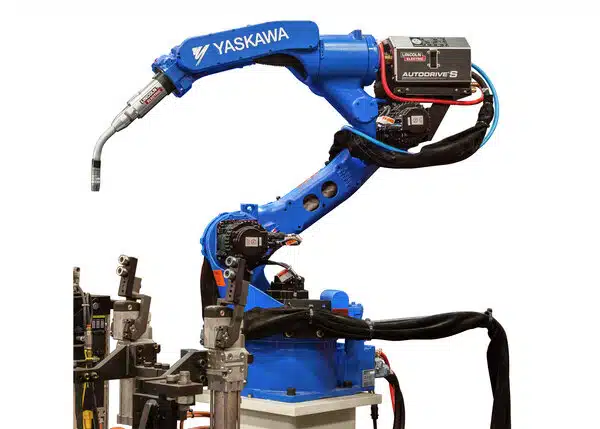

The motor’s rotation is synchronized with the welding process, ensuring a consistent and continuous feed of the wire. Drive rolls, also known as feed rolls or drive rolls, are in direct contact with the wire and grip it, pushing it forward as the rolls rotate. Wire guide tubes are used to guide the wire from the wire feeder to the welding torch. The wire feeder is equipped with controls to adjust and regulate the wire feed speed.
Robotic MIG Torch
The MIG torch’s functionality in an automated MIG welding system is to precisely position the welding arc, deliver the consumable wire electrode, distribute shielding gas, and protect the weld pool. The torch is a critical element in achieving accurate and consistent welds, and its design and features may vary based on the specific welding application and system requirements.
The MIG torch is a fundamental component in an automated MIG welding system. It serves as the delivery mechanism for the welding arc, shielding gas, and consumable wire electrode.
MIG Robotic Arm Or Positioner
The robotic arm or positioner in an automated MIG welding system is responsible for manipulating and controlling the welding torch’s movement and positioning weld cells.
It executes programmed welding paths, handles complex welding patterns, operates at high speeds, and integrates with sensors and vision systems for enhanced control and adaptability. The robotic arm’s precision and efficiency contribute to achieving accurate, consistent, and efficient welds in automated MIG welding processes.
The robotic arm or positioner can be integrated with sensors and vision systems to enhance the welding process.
These systems provide real-time feedback on variables such as torch position, arc stability, and workpiece condition. This feedback enables adaptive control, ensuring accurate weld placement and compensating for any variations or deviations.
Sensor System
The sensor system in an automated MIG welding system plays a crucial role in monitoring and controlling the welding process in industrial environments. It provides real-time feedback on various parameters to ensure accurate and consistent welds.
By providing real-time feedback on critical parameters, the sensor system ensures that the automated MIG welding process operates within desired specifications. It enables precise control, monitors the welding conditions, and facilitates adaptive adjustments, resulting in accurate, consistent, and high-quality welds.
Robotic Welding Control System
The control system in an automated MIG welding system plays a vital role in overseeing and regulating the welding process. It acts as the central hub that coordinates and manages various components to ensure accurate and consistent welds.
The control system is responsible for regulating and adjusting the welding process parameters, executing programmed sequences, incorporating closed-loop feedback for continuous adjustments, and facilitating adaptive control. It ensures precise control, consistency, and quality in the welding operation, while also offering monitoring, integration, and data analysis capabilities for process optimization and quality improvement.
Shielding Gas Supply
The shielding gas supply in an automated MIG welding system provides a controlled atmosphere around the arc and weld zone. It protects the weld pool from atmospheric contamination, preventing defects and ensuring high-quality welds. The gas supply system includes gas selection, cylinder storage, gas delivery, flow control, nozzle or diffuser design, and the ability to adjust gas composition. Proper shielding gas supply and control are essential for achieving consistent, clean, and defect-free welds in automated MIG welding processes.
MIG Vs TIG Welding Automation
MIG (Metal Inert Gas) and TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) are two commonly used welding processes, and both can be automated for increased efficiency and precision.
MIG automation and TIG automation differ in their process principles, equipment requirements, welding applications, weld quality, and their ability to handle joint complexity.
MIG automation excels in high-speed production with good weld quality, while TIG automation offers superior weld aesthetics and control, particularly for intricate and critical applications.
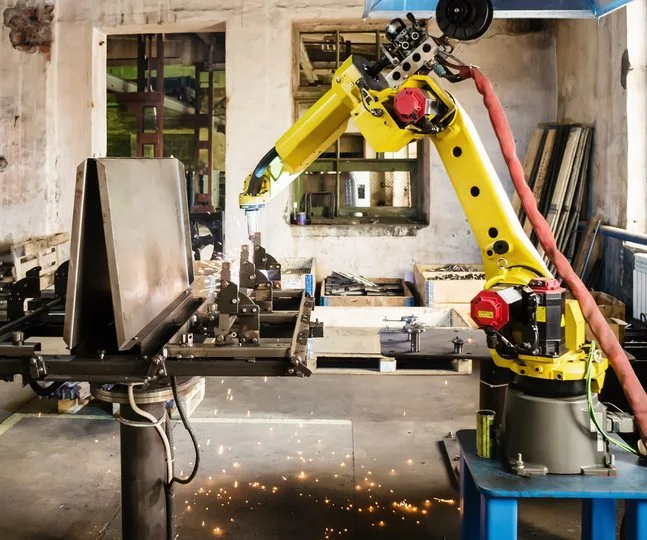

The choice between MIG automation and TIG automation depends on the specific welding requirements, materials, joint designs, and desired weld characteristics. MIG automation is often preferred for high-speed welding applications that involve thick materials or long, continuous welds. It is commonly used in industries such as automotive, fabrication, and manufacturing, where speed and efficiency are important.
TIG automation is typically chosen for applications that demand higher-quality welds and precise control, such as aerospace, nuclear, and specialized industries. It doesn’t use a non-consumable welding wire, but filler material to produce welds.
Is Automated MIG Worth Investment?
Investing in automated MIG welding can be worth it for many businesses, depending on their specific needs and circumstances. It’s essential to conduct a thorough analysis of your specific business requirements, production needs, and financial considerations before making an investment decision.
Assessing the potential benefits, cost savings, and long-term advantages of automated MIG welding can help determine if it is worth investing in for your particular business.
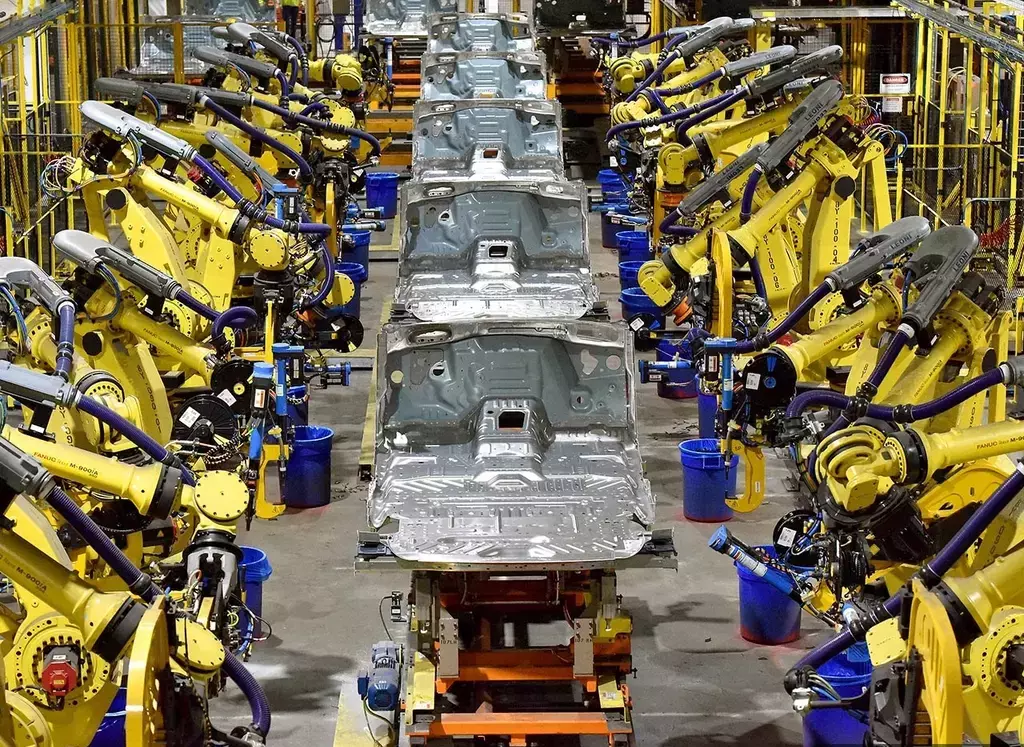

While the initial investment in automated MIG welding equipment may be significant, it can lead to long-term cost savings. Automation reduces labor costs, improves productivity, and minimizes material waste and rework. Assessing the potential ROI involves considering factors such as production volume, labor costs, scrap rates, and increased efficiency.
Automated MIG welding reduces the reliance on manual labor. If your business is facing challenges with finding skilled welders or dealing with high labor costs, automation can be a cost-effective solution for high-volume production runs. Automated systems can operate with minimal human intervention, reducing labor expenses and freeing up skilled welders for more complex tasks.
Conclusion
Automated MIG welding offers significant advantages in productivity, quality control, and cost savings. It streamlines production processes, ensures consistent weld quality, and reduces labor costs. The ability to handle high volumes with minimal human intervention improves efficiency and mitigates safety risks.
While requiring an initial investment, the long-term benefits of reduced rework, increased profitability, and adaptability to changing market demands make automated MIG welding a worthwhile investment. By leveraging advanced technology and robotic systems, businesses can achieve higher productivity, superior weld quality, and improved competitiveness in the manufacturing industry.
Resources
- https://tec-option.com/mig-welding-automation/
- https://howtorobot.com/expert-insight/mig-welding-robots
- https://www.robots.com/applications/mig-welding
- https://www.marlinwire.com/robotic-tig-and-mig-welding
- https://www.genesis-systems.com/blog/robotic-mig-vs-tig-welding-choosing-right-robotic-welding-application