TIG welding equipment is a big investment, and it must be appropriate for the application at hand. Additionally, the machine must be maintained diligently to ensure it will perform when needed.
But, what about the other parts of the welding system? There are factors to consider for those components as well, especially the TIG welding torch.

The torch used for the gas tungsten arc welding process is an integral part of the welding system, and it is responsible for carrying and directing the welding current to the weld joint.
So it is important to take a few moments to consider the tips that will help you when choosing the right TIG torch.
The TIG Welding Torch: From the Welding Machine Forward
Choosing a durably constructed TIG torch that has reliable components and properly maintaining that torch can save a lot of hassle and frustration. Plus, it’ll keep you welding longer, and, giving your torch purchase adequate consideration can help lower costs for replacements.
However, there is no hard rule for selecting the right torch. There are only factors to consider with each component. The selection will depend on the appropriate application, and that’s why we gathered some recommended guidelines.
The TIG torch Handle
The GTAW torch has to have the right handle for the job to increase comfort. Specifically, the handle should feel comfortable in your hand and should offer the cooling capacity for the required application. Most commonly, TIG torches utilize two types of handles: smooth, which are sometimes called knurled, or ribbed.
Ribbed handles improve cooling capacity on air-cooled torches, and often are standard you get once you buy an air-cooled GTAW torch. Conversely, smooth handles offer good thermal conductivity for water-cooled torches.
The handles can be interchanged according to welding operator preference.
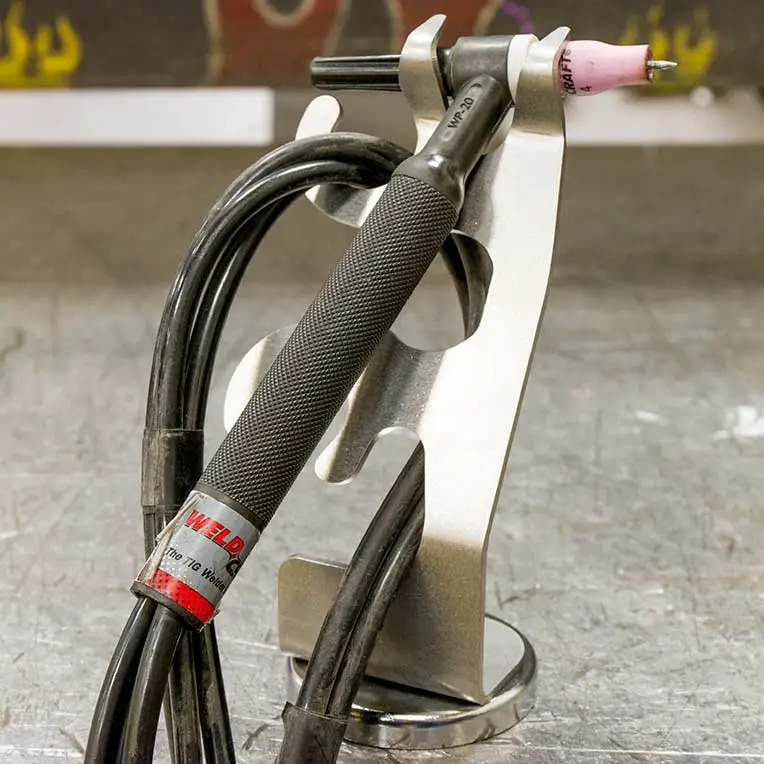

However, it is important that both are made of durable electrical grade plastic. This compound helps resist cracking and protects against high-frequency shocks.
If the used welder does not have a gas solenoid, choose a torch body that includes a gas valve control. This valve can be turned on and off as needed, which prevents unnecessary shielding gas usage. As a result, this might be a definite cost-saving factor.
TIG Torch Body Insulation
The TIG torch body should offer a good insulation, which protects the torch against damage from day-to-day use. Insulation might also extend torch life and shields against high-frequency leakage.
Most TIG torch manufacturers use silicon rubber as insulation, and some specifically use a high-dielectric type. High-dielectric silicon rubber can withstand higher voltages without damage, which prolongs the life of the torch. Silicon rubber is also more resilient than the torch body that uses hard phenolic (another torch body option) and resists cracking if dropped.
Basic Construction
Good arc stability and, with it, good welding performance of the GTAW torch body is a courtesy of a heavy copper construction. Additionally, highly-conductive copper components, such as collets and collet bodies can also help.
In particular, collets and collet bodies composed of a tellurium-copper alloy offer the best conductivity.
These components also are more resistant to heat than standard copper, and they resist twisting or elongating which holds tungsten more securely. Secure tungsten will result in a steady arc and good weld quality.
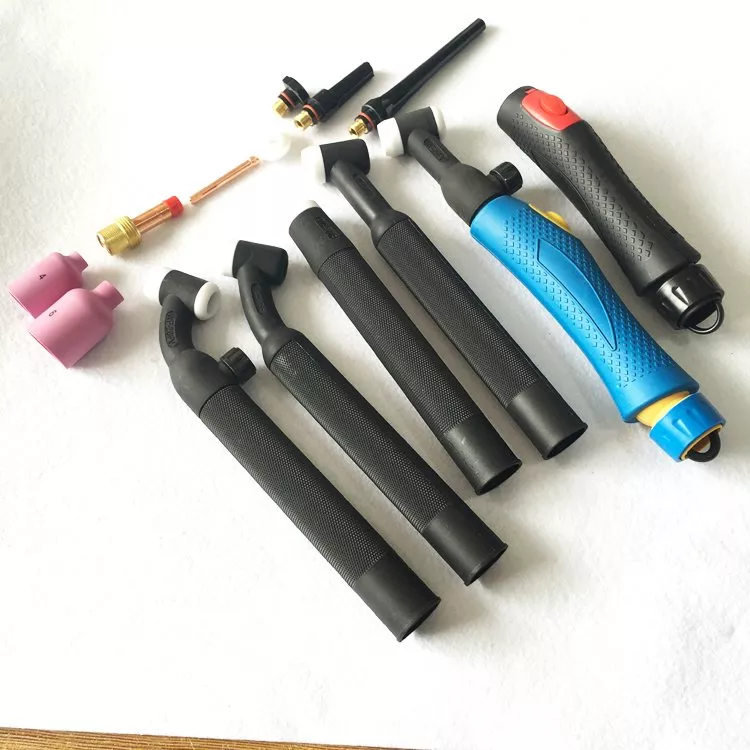

Backcaps are usually made of an assortment of phenolic compounds. They have varying degrees of heat resistance. So, select a backcap that is made of compounds that fit the amperage requirements of the welding application.
For example, if the TIG torch is used for low-duty applications, a backcap made of a low-temperature phenolic compound will do the job. On the other hand, a backcap with higher thermal resistance is suitable for more demanding applications.
Gas Coverage And Nozzles
If your particular GTAW application requires greater shielding gas coverage, or joint access is limited, you can add a gas lens to the TIG torch head. Select a gas lens made of durable porous media, rather than those made of multiple thin screens. These gas lenses are more expensive, but they last longer and provide improved gas coverage. Using a gas lens made of porous media can result in reducing unnecessary downtime and its associated costs.
When choosing the right TIG torch, selecting the right nozzle for the application is also an important factor. Lava nozzles offer good crack resistance for medium-amperage applications, while silicon nitrate nozzles are suited for high-duty cycle TIG welding applications that work at high amperages.

Both are more expensive than alumina oxide nozzles that are suitable for low amperage applications, but they add value since they are better at resisting cracking and melting.
TIG torches with a flexible neck help to improve access to difficult joints. A gas lens with durable porous media provides good gas coverage and lasts longer than multiple screen versions. Check water-cooled TIG torches periodically for leaks that can lead to overheating and torch damage.
TIG Torch Hoses
There are two options when selecting hoses or cables for a GTAW torch. You can choose vinyl or rubber, as they are available for both air-cooled or water-cooled TIG torches. For each type of TIG torch, rubber hoses and cables, especially braided ones, are recommended due to longevity and excellent welding performance.
Rubber hoses and cables offer good heat resistance, up to 300 degrees F, compared to 150 degrees to 200 degrees F for vinyl.
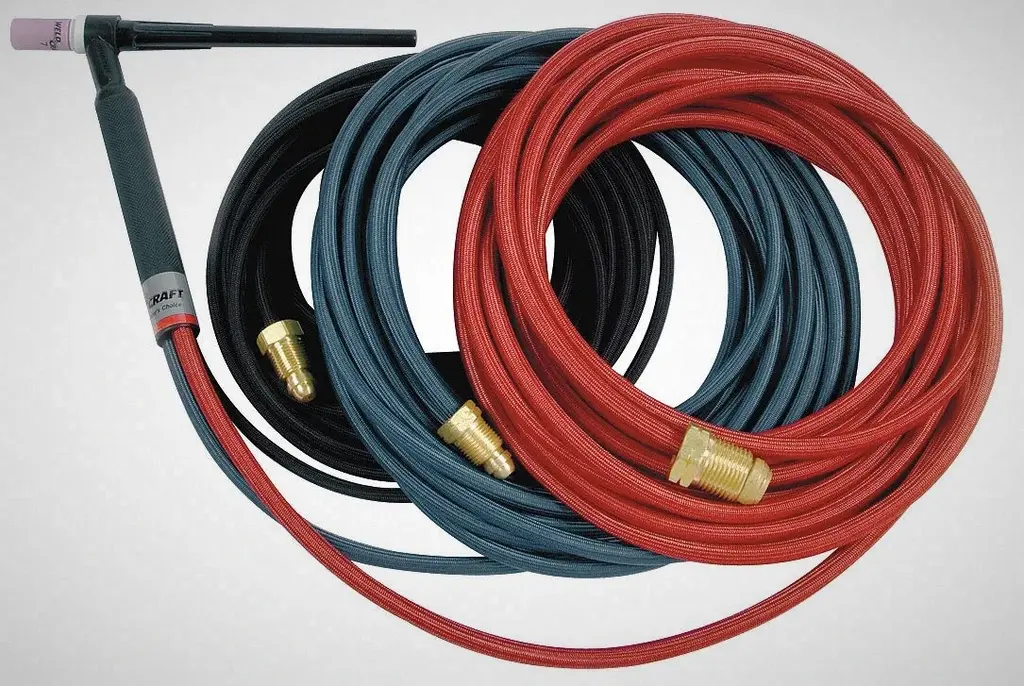

In addition, they also resist kinking. The resistance to kinking helps to prevent disruption to the shielding gas flow that can lead to problems in the weld puddle, such as porosity.
Rubber hoses and cables maintain flexibility and durability in cold environments and offer good protection against high-frequency leakage. On the other hand, vinyl hoses and cables are less expensive, are and practical for light-duty TIG welding applications. However, they do not last as long as rubber.
Water-cooled TIG torches or Air-cooled torches
Besides regular parts, you’ll also need to determine whether an air- or water-cooled TIG torch is best suited for the application. As a rule, welders prefer an air-cooled torch for lower amperage applications under 200 amps, and a water-cooled torch is used for applications that require more than 200 amps.
Air-cooled torches are heavier because they rely on the surrounding air to cool them, so make sure to select one with a comfortable handle. It will help make your air-cooled TIG torches easier to use and maneuver.

You should also consider a place of welding. Outdoor welding applications require a portable air-cooled GTAW torch, while shop applications can accommodate a water-cooled torch with an appropriate water cooler better.
Keep in mind that most TIG torches offer flexible necks. These can be ordered from most TIG torch manufacturers, and they are suitable when you have particularly tight joints to weld or for welding in awkward positions.
Some torch body styles feature a modular design. This allows a flexible head to be added, which allows the use of the different heads. These types of modular TIG torches work well when dealing with complex joints and applications that require reaching a variety of different angles. Modular GTAW torches also can help to lower costs by allowing you to customize a single GTAW torch to the TIG process instead of having to buy a different torch for each application.
Remember, a TIG torch, no matter the application, plays an important part in the overall TIG welding process. So besides the TIG machine, you will also need a suitable torch for the best TIG weld. However, you won’t have that much problems when choosing a MIG torch.
That’s why experienced welder will take care to select one that meets their needs and that complements the TIG welder. It will save time, money, and a lot of headaches.
Ten Easy Tips for Maintaining a GTAW Torch
Once you’ve chosen the most appropriate GTAW torch and components for your application, routine inspections and some simple maintenance can help make them last.
- To protect hoses and cables from cuts caused by dragging, use a woven nylon cable cover with a plastic zipper. These can also help you avoid high-frequency problems that can lead to torch damage.
- To remove oxides that can lead to an erratic arc and shorten consumable life, periodically remove the collet and collet body and clean them with a wire brush.
- Make sure all threads on connecting points of the torch are tightened properly. That way, you will prevent problems with an electrical conductivity that might damage the torch’s front-end parts.
- Visually inspect the nozzle to make sure there is no distortion, cracking or blackening. These signs of wear can lead to improper gas coverage, so you will have to replace the nozzle
- Check for cracks in the handle by inserting a wooden dowel or your finger into the back end of the torch. if there is some damage, replace the handle – do not tape to avoid injury from shocks.
- Visually inspect the silicon rubber insulation surrounding the torch body for any cuts. Replace if any irregularities are found.
- Looks for cracks or signs of deterioration on the insert, or O-ring, attached to the back cap. If needed, replace to prevent aspiration (pulling of air into the torch body).
- Keep the threads connecting the backcap and torch body clean, look for any signs of wear on the threads, and replace them as necessary.
- Test that the power connector is tightened to the power source to prevent overheating and damage to the torch cable. Also, be certain all gas and water fittings are secure to prevent leaks.
- When using water-cooled TIG torches, periodically remove the handle to check water connections for leaks that can lead to torch overheating and damage.