Cold wire TIG welding, also known as TIG cladding, is a revolutionary welding technique that allows you to weld two pieces of metal together without generating any sparks or splatter.
This welding process can produce highly precise and clean welds, even on thin and delicate materials.

This advanced welding process uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode and a separate wire feeder to deposit a cold filler metal onto the workpiece. The result is a welding process that is incredibly versatile, efficient, and environmentally friendly. In this article, we’ll explore the benefits of cold wire TIG welding and how it can be used in various industries.
What Is Cold Wire TIG, And How Does It Work?
Cold wire TIG welding unlike Hot Wire TIG is a welding process that uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode to create an electric arc between the workpiece and a separate wire feeder that provides cold filler metal. This process is also known as TIG cladding or TIG overlay welding.
The non-consumable tungsten electrode is held in a torch, and an inert gas, such as argon, is used to protect the weld from atmospheric contamination.
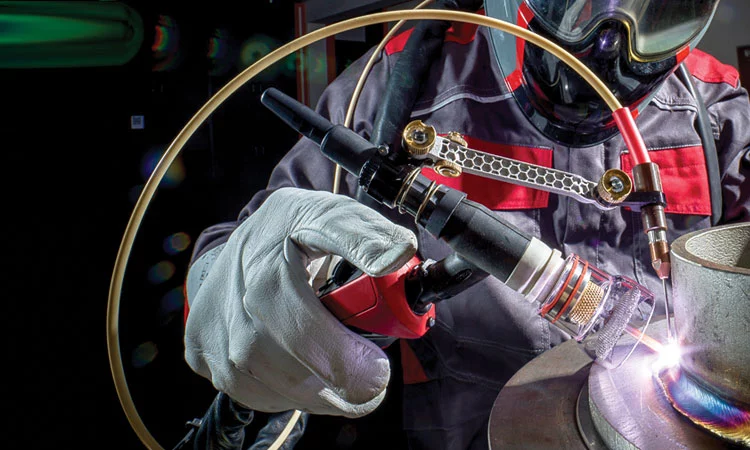

The separate wire feeder provides a controlled and precise amount of filler metal to the workpiece. Unlike traditional TIG welding, which uses a consumable electrode to both create the arc and provide the filler metal, cold wire TIG welding separates these two processes. The result is a welding process that is highly precise and efficient, with minimal heat input to the workpiece.
The cold filler metal that is fed into the arc does not melt until it reaches the workpiece. This means that the filler metal is added to the weld in a solid state, creating a clean and precise weld with minimal distortion. The precise control over the amount and location of the filler metal allows for highly accurate welds, even on thin and delicate materials.
Cold wire TIG welding is commonly used in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and medical device manufacturing, where precision and quality are critical. It can be used to weld dissimilar materials, such as titanium to stainless steel, and can produce welds with excellent mechanical properties and corrosion resistance.
Are Cold Welding And Cold Wire TIG Welding The Same?
Cold welding and cold wire TIG welding are two different processes that have different applications and characteristics.
Cold welding is a process of joining two metal surfaces together without heat or the use of any filler metal. It relies on the natural attraction between the atoms of two clean metal surfaces to create a strong bond.
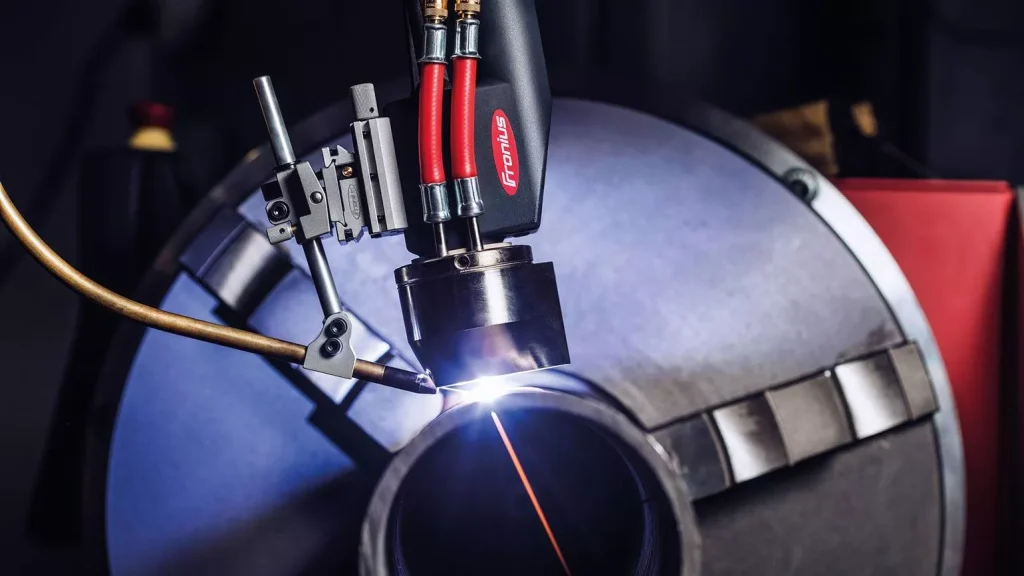

This process is typically used for joining small parts or wires and is commonly used in the electronics and aerospace industries. Cold wire TIG welding, on the other hand, is a welding process that uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode to create an electric arc between the workpiece and separate cold wire feeders that feed filler wire directly to the weld.
The filler metal is added to the weld in a solid state, creating a clean and precise weld with minimal distortion. This process is commonly used in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and medical device manufacturing, where precision and quality are critical.
TIG Cold Wire Equipment
Cold wire TIG welding requires specialized equipment that is designed for this specific welding process. Besides standard shielding gas supply, and tungsten, it is important to select equipment that is appropriate for the specific welding application and to ensure that all equipment is properly maintained and calibrated. To successfully use it, you will need a TIG wire feeder, filler wire, and welding Torch.
TIG Welder For Cold Wire
A TIG welder or power source for cold wire TIG welding should have precise and stable current control, a pulsed DC output, a high-frequency start, and precise gas flow control. These features allow for precise control over the welding process and help to ensure clean and precise welds with minimal distortion.
- Current Control: The TIG welder should have precise and stable current control that can be adjusted based on the specific welding application. This is important for maintaining consistent arc stability and for producing clean and precise welds.
- Pulsed DC Output: A pulsed DC output is preferred for cold wire TIG welding. This allows for precise control over the amount of heat being introduced to the workpiece and helps to prevent distortion and warping.
- High-Frequency Start: A high-frequency start is preferred for cold wire TIG welding. This helps to ensure a stable arc initiation and reduces the likelihood of tungsten electrode contamination.
- Gas Flow Control: The TIG welder should have precise gas flow control to ensure that the weld is properly shielded from atmospheric contamination.
Cold Wire Feeder
The TIG cold wire feeder is an accessory that is used in conjunction with a TIG welding machine to supply a separate wire feed to the weld pool during TIG welding. The feeder is typically mounted on a separate stand or cart and is connected to the welding torch by a flexible conduit. It has its own power cable and feed cable.
The fundamental principle of the cold wire feeder is to supply a separate filler of different wire size to the weld puddle while maintaining a stable and precise arc between the non-consumable tungsten electrode and the workpiece. This is achieved by using a remote wire feeder that can be operated independently of the welding torch.

The cold wire feeder consists of several components, including the wire spool, the wire feed motor, the drive rollers, and the wire guide. The spool of cold filler wire is mounted on the feeder, and the wire feed motor rotates the spool to supply the wire to the drive rollers. The drive rollers grip the wire and feed it through a flexible conduit to the welding torch.
The wire guide is an important component of the cold wire feeder. It is typically a small device that is mounted on the welding torch and guides the wire into the weld pool. The wire guide should be designed to provide precise control over the location and amount of filler wire is added to the weld.
The cold wire feeder is typically controlled by a foot pedal or a hand control that allows the welder to adjust the feed rate of the filler wire. The feed rate can be adjusted based on the specific welding application and the size of the filler wire being used.
One of the main advantages of the cold wire feeder is the ability to precisely control the amount and location of the filler metal being added to the weld pool. This allows for clean and precise welds with minimal distortion when feeding multiple wire sizes. Additionally, the use of a separate filler wire reduces the likelihood of tungsten electrode contamination, which can be a common problem in traditional TIG welding.
Cold Wire Filler
Cold wire TIG welding uses a variety of filler metals, including stainless steel, aluminum, and nickel alloys, depending on the specific welding application. The selection of filler metal is typically based on the properties of the base metal being welded and the desired mechanical properties of the finished weld.
The diameter of the cold wire used in cold wire TIG welding can vary depending on the specific application. Typically, the diameter of the wire used ranges from 0.030” through 1/8” (0.9 to 3.2 mm) of hard and soft wires for mechanized TIG or plasma welding.
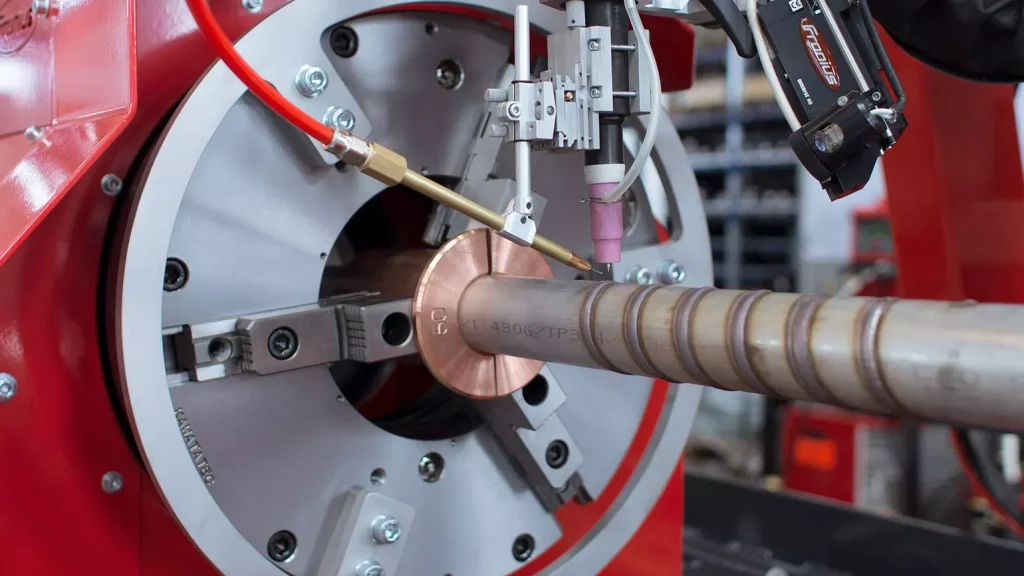
The specific diameter of the wire used will depend on the size of the weld joint, the thickness of the base metal, and the welding technique being used. The fundamentals of cold wires used in cold wire TIG welding include the composition of the wire, the type of coating on the wire, and the surface finish of the wire.
The composition of the wire is critical in determining the mechanical properties of the finished weld. The coating on the wire helps to protect it from oxidation during storage and transport and can also affect the welding characteristics of the wire. The surface finish of the wire is important for ensuring smooth and consistent wire feed through the cold wire feeder.
TIG Welding Torch
For cold wire TIG welding, a TIG torch with a built-in cold wire feeder or a separate cold wire feeder attached to the torch is typically used. The torch must be capable of accommodating a separate cold wire feed, which requires a larger torch body and a flexible conduit that connects the feeder to the torch.
The TIG torch for cold wire TIG welding, such as the CK TIG torch, typically has a modified gas cup, torch outfit, and a wire guide that is mounted on the front of the torch to guide the cold wire into the weld pool.
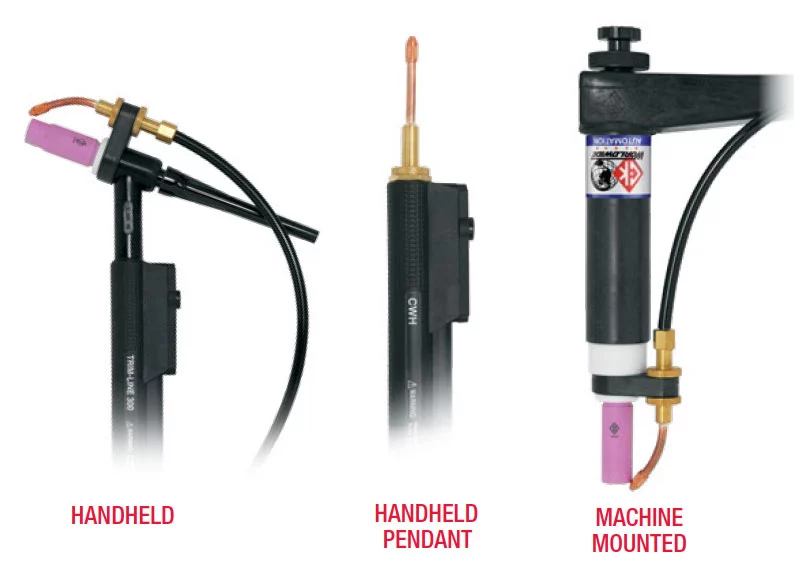

The wire guide must be precisely aligned with the tungsten electrode to ensure proper wire placement and arc stability. The gas cup on the TIG torch used for cold wire TIG welding may be larger than that used for traditional TIG welding to provide additional gas coverage for the larger torch body and the cold wire feed. The gas flow rate must be adjusted to provide adequate shielding gas coverage for the weld pool and to prevent oxidation of the filler wire.
The TIG torch used for cold wire TIG welding may also require a special heat shield to protect the feeder motor and drive rollers from the heat generated during welding. The heat shield should be designed to provide adequate cooling and ventilation for the feeder while maintaining a safe working temperature for the operator.
Advantages Of Cold Wire TIG Welding
Cold wire TIG welding offers several advantages over traditional TIG welding, including:
- Improved Weld Quality: Cold wire TIG welding provides precise control over the amount and placement of filler metal, resulting in consistent and uniform welds. The use of cold wire also reduces the heat input to the workpiece, minimizing distortion and reducing the risk of heat-related defects.
- Increased Productivity: Cold wire TIG welding can increase productivity by reducing the need for frequent filler metal changes and reducing the time required to complete a weld. The use of a cold wire feeder also eliminates the need for the welder to manually feed filler wire, reducing operator fatigue and improving overall efficiency.
- Enhanced Weld Appearance: Cold wire TIG welding produces a smooth and consistent weld bead with minimal spatter and a uniform appearance. This makes it ideal for applications where appearance is important, such as in the food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic industries.
- Cost Savings: Cold wire TIG welding can result in cost savings by reducing material waste, improving process efficiency, and reducing the need for post-weld processing. The use of cold wire also reduces the amount of filler material required, resulting in lower material costs.
- Versatility: Cold wire TIG welding can be used with a wide range of materials, including stainless steel, aluminum, and nickel alloys, making it suitable for a variety of welding applications.
Drawbacks of Cold Wire TIG Welding
While cold wire TIG welding offers many advantages, there are also some potential drawbacks to consider:
- Equipment Cost: The cost of the equipment needed for cold wire TIG welding can be higher than that of traditional TIG welding equipment. This includes the cost of a cold wire feeder, a larger TIG torch, and other accessories, which are sold separately.
- Complexity: Cold wire TIG welding requires more complex equipment and setup than traditional TIG welding, which may require more training and experience to operate and time for complete installation. However, with it, even less experienced welders can achieve excellent results.
- Maintenance: The cold wire feeder used in cold wire TIG welding requires regular maintenance, including cleaning and lubrication, to ensure reliable performance.
Applications of Cold Wire TIG
Cold wire TIG welding is a versatile process that can be used in a variety of applications across many industries. Some common applications of cold wire TIG welding include:
- Aerospace: Cold wire TIG welding is used in the aerospace industry to weld thin-walled components, such as fuel tanks and engine components.
- Automotive: Cold wire TIG welding is used in the automotive industry to weld exhaust systems, suspension components, and other parts that require precise and uniform welds.
- Medical: Cold wire TIG welding is used in the medical industry to weld stainless steel and other high-quality materials for medical devices and equipment.
- Food and Beverage: Cold wire TIG welding is used in the food and beverage industry to weld stainless steel equipment, such as tanks, conveyors, and processing machinery, that require clean and uniform welds.
- Pharmaceutical: Cold wire TIG welding is used in the pharmaceutical industry to weld stainless steel equipment, such as tanks, piping, and fittings, that require clean and consistent welds.
- Energy: Cold wire TIG welding is used in the energy industry to weld pipes, boilers, and other equipment used in power generation and distribution.
Conclusion
Cold wire TIG welding is a versatile and precise welding process that offers several advantages over traditional TIG welding. By using a cold wire feeder and precise weld parameters, the process allows for greater control over the amount and placement of filler metal, resulting in consistent and uniform welds with minimal heat input.
This can lead to improved weld quality, increased productivity, enhanced weld appearance, and cost savings. While there are some potential drawbacks to consider, such as equipment cost and limited wire feed rates, cold wire TIG welding remains an attractive option for many welding applications across various industries.
Resources
- https://www.dfmachinespecialties.com/tig-torches/tig-cold-wire-feed-attachment
- https://stainless-steel-world.net/cold-wire-tig-welding-smart-and-simple/
- https://www.fronius.com/en/welding-technology/product-information/iwave-tig-welding-system/tig-dynamicwire
- https://www.cruxweld.com/blog/cold-welding-machine/
- https://www.twi-global.com/technical-knowledge/faqs/what-is-cold-welding