In today’s world of technological advancements, remote work has become the norm, and welding is no exception.
Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) welding, a precise and intricate welding process, is now being performed remotely, offering many benefits over traditional welding methods.

With the use of advanced technologies such as augmented reality and remote control welding systems, welders can perform highly skilled welding operations on critical infrastructure from anywhere in the world. In this article, we will explore the world of remote TIG welding and how it’s revolutionizing the welding industry.
What Is Remote Welding?
Remote welding is a process where a welding machine is operated by a welder who is not physically present at the job site. Instead, the welder uses remote controls to adjust the machine through various technologies such as the internet, wireless networks, or satellite connections.
Remote TIG welding is used when the welding operation requires highly skilled welders to work on critical infrastructure such as oil rigs, pipelines, and nuclear power plants that are located in remote or hazardous locations.

The use of remote TIG welding eliminates the need for welders to travel to these locations, reducing travel expenses, and increasing productivity. Remote welding requires a high level of skill and expertise, as the welder must have a thorough understanding of the welding process, metallurgy, and welding codes and standards. The process involves controlling the arc, filler material, and shielding gas remotely to ensure a precise and high-quality weld.
The use of advanced technologies such as augmented reality and remote control welding systems has made remote TIG welding more efficient and effective. These technologies allow the welder to see the welding operation in real time, providing a clear and accurate view of the welding process. Additionally, remote control welding systems offer features such as automatic arc length control and wire feeding, which increase the accuracy and speed of the welding process.
Simple Remote Applications For TIG Welding
Remote amperage control with a TIG torch is achieved by attaching a remote amperage control device to the torch. This device allows the welder to adjust the amperage with their other hand while they hold the torch in the other hand. This is particularly useful in situations where the welder needs to move around while welding or when the foot pedal is not accessible.
In TIG welding, the amperage (or current) used to create the arc is a critical variable that affects the quality and appearance of the weld. Traditionally, the amperage is controlled by a foot pedal, which the welder steps on to increase or decrease the amperage. However, with remote amperage control, the welder can adjust the amperage using a TIG torch remote control instead of a foot pedal.

The remote amperage control device typically consists of a small hand-held device with a knob or button that the welder can use to adjust the amperage. The device is connected to the TIG welding machine by a cable, which allows the welder to control the amperage remotely.
Remote amperage control with a TIG torch offers several advantages over using a foot pedal. For one, it provides greater mobility and flexibility during the welding process, allowing the welder to move around and adjust the amperage as needed. Additionally, some welders find it more comfortable to use a TIG torch remote control because it eliminates the need to keep their foot on a pedal for an extended period.
Remote Foot Control
The foot pedal is a common device used to control the amperage in TIG welding. The foot pedal is connected to the TIG welding machine by a cable and pin plug (make sure that size fits the welder), and the welder steps on it to increase or decrease the amperage. The foot pedal controls a variable resistor, which regulates the amount of current flowing through the welding circuit.
To use a foot pedal to control the amperage in TIG welding, the welder first sets the machine to the desired amperage range.

They then place the electrode near the workpiece and step on the foot pedal to start the arc. As they weld, they can adjust the amperage by pressing down harder or releasing the pedal slightly.
Two Main Types Of Foot Pedals Used In TIG Welding
- Analog foot pedals: Analog foot pedals use a variable resistor to control the amperage. When the welder presses down on the pedal, it increases the resistance, which in turn decreases the amperage. When the welder releases the pedal, the resistance decreases, and the amperage increases.
- Digital foot pedals: Digital foot pedals use electronics to control the amperage. When the welder presses down on the pedal, a signal is sent to the TIG welding machine, which then adjusts the amperage accordingly. Digital foot pedals offer greater accuracy and repeatability than analog foot pedals, and they are often preferred by professional welders. These are found in advanced machines such as Miller Diversion.
Controlling the amperage with a foot pedal requires a high level of skill and coordination, as the welder must maintain a steady foot pressure while moving the TIG torch and manipulating the filler metal. Foot pedals also require the welder to remain in a fixed position, which can be tiring over long welding sessions.
Why Choose Foot Pedal Remote Amperage Control Over Other Options?
While remote control options, such as a TIG torch remote control, offer greater mobility and flexibility in controlling the amperage in TIG welding, foot pedals still have some advantages that make them the preferred choice in certain situations.
For one, foot pedals offer a tactile feedback that allows the welder to feel the changes in amperage as they press down or release the pedal.
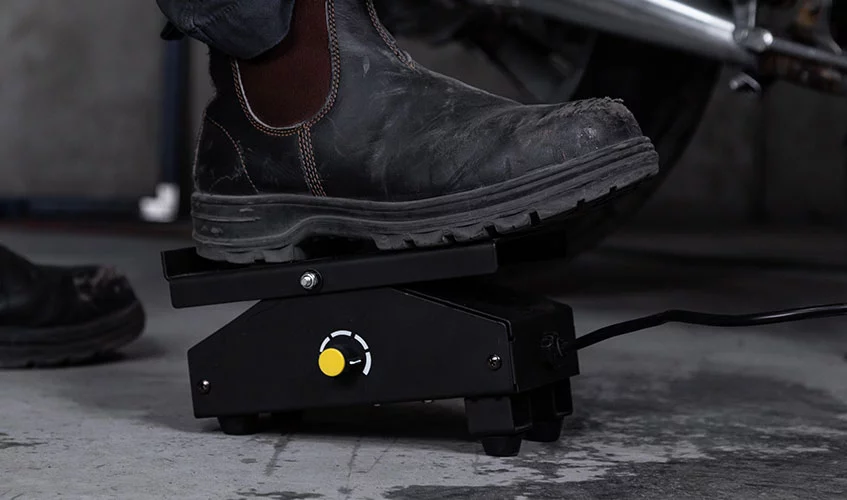

This feedback can be particularly useful in situations where precise control of the amperage is required, such as when welding thin or delicate materials. Foot pedals are also relatively simple and easy to use, requiring minimal training or setup time. They are widely available and compatible with most TIG welding machines, making them a convenient option for most welders.
Finally, foot pedals are often less expensive than other types of remote control options, making them an attractive option for hobbyists or welders on a budget.
Wireless Foot Pedals
Wireless foot pedals are a type of remote control device used in TIG welding that allow the welder to control the amperage without the need for a physical cable connection between the pedal and the welding machine. Wireless foot pedals use radio waves or Bluetooth technology to transmit signals to the welding machine, allowing the welder to control the amperage from a distance.
The advantages of using a wireless foot pedal include greater mobility and flexibility, as the welder is not tethered to a cable and can move around more freely. This can be particularly useful in situations where the welder needs to move around the workpiece or in tight spaces where a cable could get in the way.
Wireless foot pedals also eliminate the need for cable management, which can be a significant source of frustration and can impede the welder’s movement during welding.
Another advantage of wireless foot pedals is that they eliminate the risk of tripping over the cable or accidentally pulling it out of the welding machine, which can disrupt the welding process and potentially damage the equipment. Wireless foot pedals are also relatively easy to set up and use, with most models requiring only a simple pairing process with the welding machine.
Remote Fingertip Control
Remote fingertip amperage control on a TIG torch is another type of remote control device that allows the welder to adjust the amperage using a button or dial located on the torch itself. The control is often located on the handle of the TIG torch and can be operated with a fingertip while the welder is manipulating the torch and filler metal.
The fingertip current control works by sending signals to the TIG welding machine, which adjusts the amperage accordingly. The control may allow the welder to increase or decrease the amperage incrementally or make larger adjustments, depending on the model.
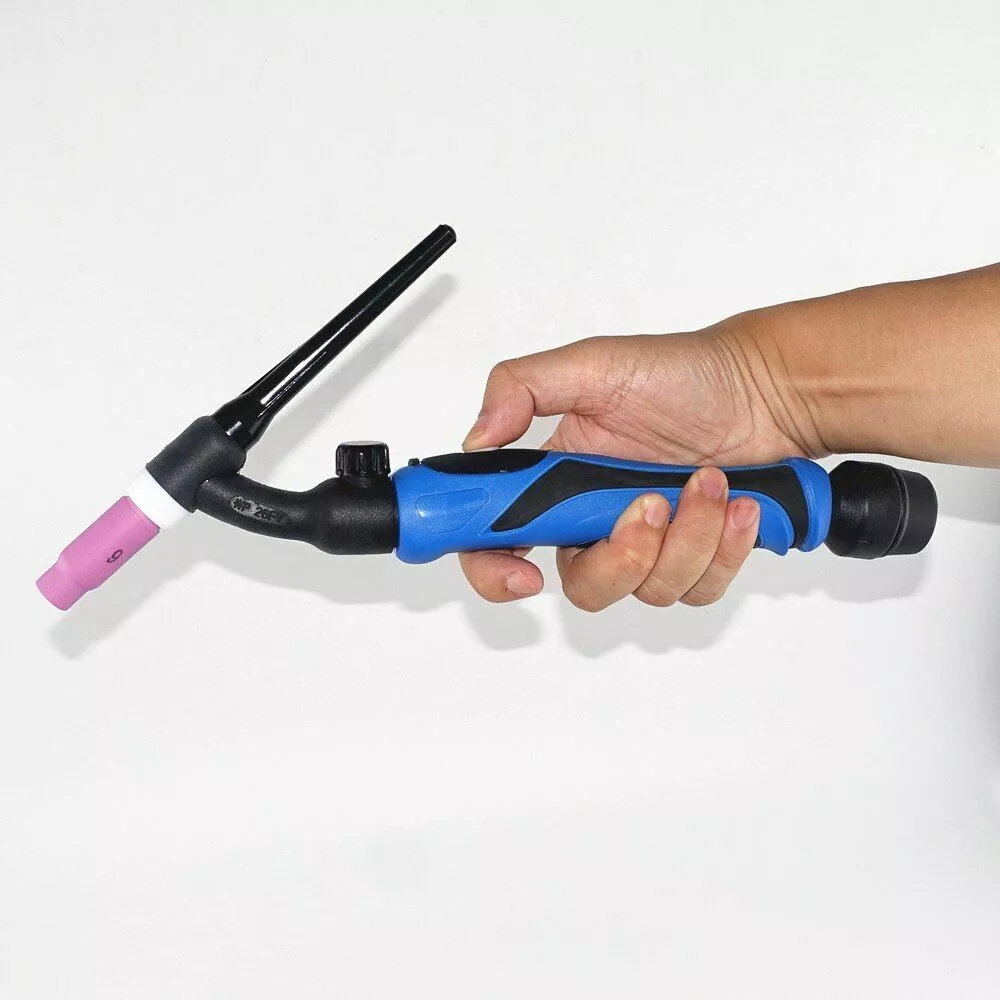

Remote fingertip amperage control is particularly useful in situations where the welder needs to make frequent adjustments to the amperage while welding. With the control located on the torch, the welder can make adjustments quickly and easily without needing to reach for a foot pedal or other remote control device.
Another advantage of remote fingertip amperage control is that it allows the welder to maintain better control over the welding process. By adjusting the amperage on the fly, the welder can ensure that the weld puddle remains consistent and that the weld penetrates the workpiece to the correct depth.
Remote fingertip amperage control is often used in conjunction with foot pedals or other remote control devices, allowing the welder to choose the control option that best suits the welding situation.
When Do You Choose Fingertip Control Over Foot Controls?
Remote fingertip control on a TIG torch and foot pedals both have their advantages and disadvantages, and the choice between the two largely depends on the welding situation and the preferences of the welder. However, there are a few situations where remote fingertip control may be preferred over foot pedals.
One situation is when the welder needs to maintain a consistent welding position over an extended period.

With remote fingertip control, the welder can adjust the amperage without having to move their foot, which can be especially helpful when welding in awkward positions to improve strain relief prevents or when welding for long periods.
Another situation where remote fingertip control may be preferred is when the welder needs to make frequent or rapid amperage adjustments. With the control located on the TIG torch, the welder can make quick adjustments without taking their hand off the torch, allowing for greater control and efficiency.
Additionally, some welders simply prefer the feel and responsiveness of remote fingertip control over foot pedals. The tactile feedback provided by the button or dial on the TIG torch can give the welder a greater sense of control over the welding process. In addition, there is a water solenoid control cord for even higher adjustments.
However, it’s important to note that remote fingertip control may not be as precise as foot pedals, as the control increments may be larger or less precise to get full amperage. Additionally, some models of remote fingertip control may be less compatible with certain TIG welding machines, limiting their usefulness in some situations.
Remote On off control
Remote on/off controls in TIG welding refer to the ability to start and stop the welding process from a remote location, without the need to physically access the TIG welding machine. These controls are typically used in situations where the welder needs to start and stop the welding process frequently, or where access to the TIG welding machine is limited or hazardous.
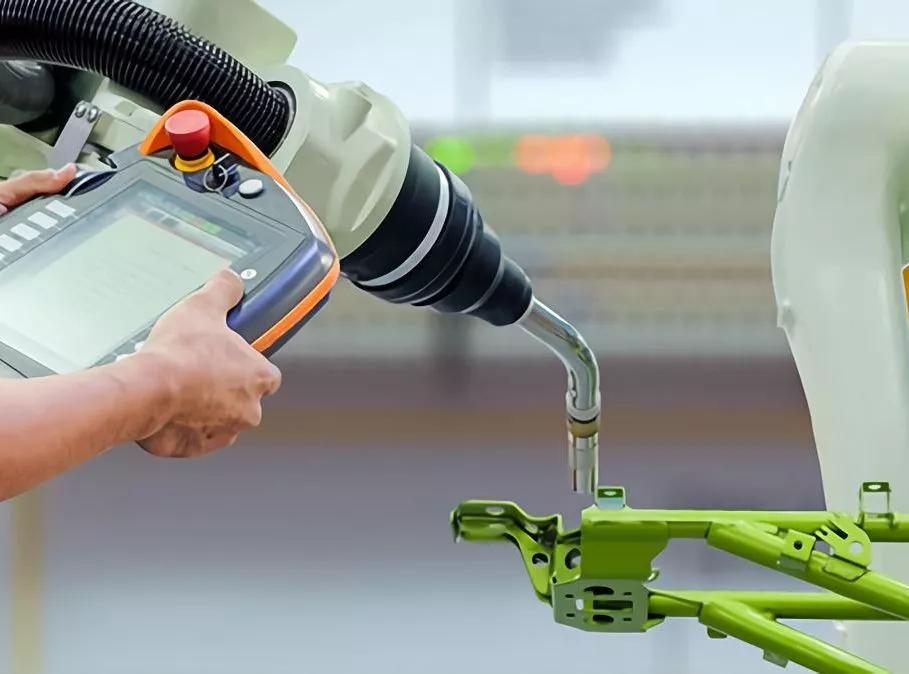
Automated TIG Welding
Automated TIG welding provides several options for remote control, allowing the welder to adjust the welding parameters without being physically present at the welding location.
This is particularly useful in situations where the welding environment is hazardous or difficult to access.

One of the most common remote control options in automated TIG welding is through a computer numerical control (CNC) system. The CNC system allows the welder to program the welding parameters, including amperage, voltage, travel speed, and wire feed rate, into the system. The system then controls the welding process automatically, adjusting the parameters as necessary to maintain consistent weld quality.
Another option for remote control in automated TIG welding is through a pendant or handheld remote control. These devices allow the welder to adjust the welding parameters, such as amperage and voltage, from a safe distance using a wireless or wired remote. The remote control sends signals to the TIG welding machine, which adjusts the parameters accordingly.
Some automated TIG welding systems also incorporate vision systems or sensors that provide real-time feedback on the welding process. These systems can automatically adjust the welding parameters in response to changes in the welding environment, such as variations in the joint geometry or the presence of contaminants.
Conclusion
Remote control options in TIG welding provide numerous benefits for welders, including improved efficiency, precision, and safety. The most common remote control options include foot pedals, remote fingertip controls, and automated TIG welding systems. Each option has its advantages and disadvantages, and the choice largely depends on the welding situation and the preferences of the welder.
Foot pedals remain a reliable and effective option for controlling amperage in TIG welding, particularly in situations where precise control is essential. Remote fingertip controls, on the other hand, may be preferred in situations where the welder needs to maintain a consistent position, make frequent or rapid amperage adjustments, or simply prefers the feel of the control. Finally, automated TIG welding provides numerous remote control options, including CNC systems, pendants, handheld remotes, and serial number sensors, that allow the welder to adjust the welding parameters from a safe distance.
Resources
- https://resources.arcmachines.com/why-use-a-remote-control-welding-unit-benefits-of-a-weld-pendant-ami/
- https://www.axxair.com/en/blog/what-is-automated-orbital-tig-welding
- https://www.wolfrobotics.com/welding-automation-solutions/robotic-tig-welding/
- https://blog.binzel-abicor.com/4-things-to-consider-before-automating-tig-welding