Since the discovery of welding in the 1800s, welding machines have gone through a series of improvements and upgrades.
Nonetheless, as a beginner, you have probably stumbled upon two main types, inverter welding machines, and transformer machines.
Transformer welding power supplies have been around since the 1930s, and some people still prefer them when working outdoors.
On the other hand, inverter welding power supply appeared in the 1990s, and today it is slowly becoming industry standard. So, let’s discuss inverter vs transformer welder differences, pros and cons, and where each type shines.
How Do Inverter welding machines Work?
An inverter works by increasing the frequency of the primary power supply from 50Hz up to 20,000 – 100,000Hz.
Electronic switches turn the power on and off extremely quickly (up to 1 millionth of a second) to do the conversion.
As a result, the inverter welder converts the AC power supply into a lower usable output voltage. For example, the 240V AC supply is converted into to 20V DC output.
Therefore inverter-based devices use a series of electronic components to convert the power. On the contrary, conventional transformer-based devices depend primarily on a large transformer to regulate the voltage.
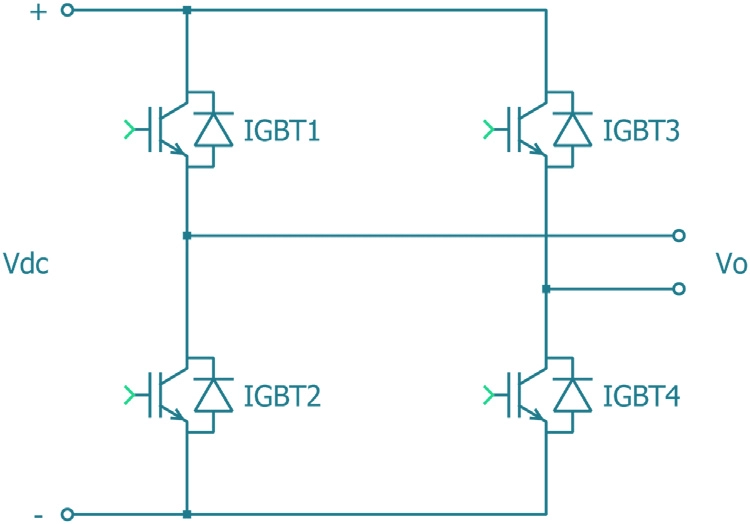
IGBT Inverter Technology
The acronym IGBT stands for “Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistors.” These are high-speed switching devices that facilitate voltage regulation.
Keep in mind that some inverter machines use older MOSFET technology. However, IGBTs are less vulnerable to mains and generator power fluctuations, making them more reliable and less prone to damage or failure.
That’s why IGBT inverter welding machines are much more common or industry standard today.
Advantages of Inverter welders
By understanding how they work, we can already see some of the advantages inverter-based machines provide. Most commonly, we are talking about the size and power efficiency, but we shouldn’t disregard the stable arc that inverter technology brings.
Size and Weight
The most noticeable difference between transformer welders and inverter machines is their size and weight.
Inverters are significantly smaller and lighter dan transformer welders since they use many electronic components instead large transformers.
Therefore, you can buy inverter welding machines that weigh less than 20 lbs to strap them on the shoulder and carry them around the workshop.
Meanwhile, transformer welding machines can weigh more than 70-80 lbs, meaning you cannot move them around without a welding cart or built-in wheels.

Inverter Efficiency
To demonstrate the efficiency differences, you should know that the inverter welding machine has a power output of up to 93% compared to conventional welding machines usually offer 60%. Therefore, the inverter welding machine utilizes more power supply, resulting in 10-15% lower electricity bills.
In addition, inverter welding machines’ efficiency is also demonstrated in higher duty cycles. For example, most inverters are rated at 60% duty cycle at maximum power output voltage, while most transformer welders offer 30%. Thus, you can work more extended periods without waiting to cool down with inverters.
Inverter Welder Performance and Consistency
The performance of quality inverter-based welders is substantially superior compared to conventional welders, and the difference is noticeable with MMA (stick/arc) welding process.
As a result, stick welding is far more manageable since you get a much easier arc start and consistent arc stability.
If you wonder why, you should know that inverter machines have higher open-circuit voltages and provide features such as hot start, anti-stick & arc-force.

These advantages are notable when welding thin materials, where using a conventional stick welder is notoriously tricky. With the infinite amperage adjustment and a very stable arc, the output can be turned down very low so that you can weld sheet metal or tube sections with relative ease & control.
Basics of Transformer welders
Transformer welders are a more traditional welding option. As the workhorse of the industry, these heavy-duty machines require mains electricity and are mainly used for industrial-grade welding applications.
A transformer-type welding power supply converts the medium voltage and moderate current electricity from the 230 or 115 VAC into a high current and low voltage supply. Most commonly, between 17 and 45 (open-circuit) volts and 55 to 590 amperes.
These achieved excellent welding and manufacturing boom after WWII, and in the period between the 1930s and 1980s, almost all arc welders were transformer-based machines. Even though they have ups and downs, if you weld mild steel all day, you won’t need to look past a transformer machine.

Advantages of Transformer welders
Even though most arc welding machines produced in the last years are inverters, transformers still got unique advantages that make them preferable to some welders. Primarily, we are talking about reliability, durability, and applications.
Transformer welder reliability
You should know transformers are reliable and rugged machines built to last.
For almost a century, transformer welding machines have proven their reliability. On the contrary, inverter machines have had only a fraction of that time—roughly 30 years, give or take. In addition, firstly-built inverter welders had many durability issues, as they used to burn a lot.
Even though today, inverter and transformer welders are both reliable, transformers still take an edge.
Transformer’s Durability
While discussing welding machines, one of the essential differences between inverters and transformers stands in terms of durability.
Airborne pollutants and high humidity can cause severe damage to inverter welders, eventually leading to premature failure.
Even though manufacturers tend to make inverter welding machines more resistant, transformer welders still thrive.
What does transformer welder durability mean to welders? Increased durability means you can use a transformer welder to weld in dusty and moist outdoor conditions. Therefore, the transformer welder is crowned as a real industry workhorse with higher power output and durability.
Welding Applications
Transformer welding machines found their way into many different industries and the welding community. However, even today, they thrive in applications such as pipeline welding, construction, or any work at the building sites.
Transformer machines are more than suitable if you are not using several arc welding techniques, and once you do the same job repeatedly.
Inverter vs transformer Welder Ultimate Breakdown
While manufacturers tried to build an ultimate welding machine that would combine the good sides of both inverter welders and transformer machines, the efforts failed since the end product was too complicated and expensive. So at the moment, the choice is still on either inverters or transformers.
Most welding experts consider your choice should be based solely on your needs and personal preferences. However, choosing might be hard for a beginner, and that’s why we made an ultimate breakdown of the pros and cons.
Welder Versatility
The electronics and software industry introduced many upgrades and technological advancements, making inverter machines capable of fine-tuning the settings and adjusting to your needs perfectly.
As a result, you get unmatched control over your inverter welder, increasing the weld quality and overall versatility and performance. Meanwhile, the transformer welder is quite capable of welding mild steel repeatedly.

However, today’s need’s often include welding “exotic” metals, which require other arc welding techniques such as improved pulsed arc TIG welding, and that’s where inverter welders work the best.
On the other hand, transformer welder usually provides higher output, making them more suitable for significantly thicker materials. Nonetheless, since we are mostly talking about home use, the inverter welding machine takes an edge in terms of versatility.
Welder Efficiency
Knowing that the inverter welder uses half the amperes to get a similar amount of volts, it is easy to say that the inverter is more efficient than the transformer welder. In addition, most inverters bring dual voltage capability, meaning you can use both 110V/220V power supply.
Since its inception, inverter welders were limited to DC power only. However, the latest improvements in the welding world made them capable of running both AC/DC power. Therefore, you get a pretty competent and efficient welding machine with an inverter.
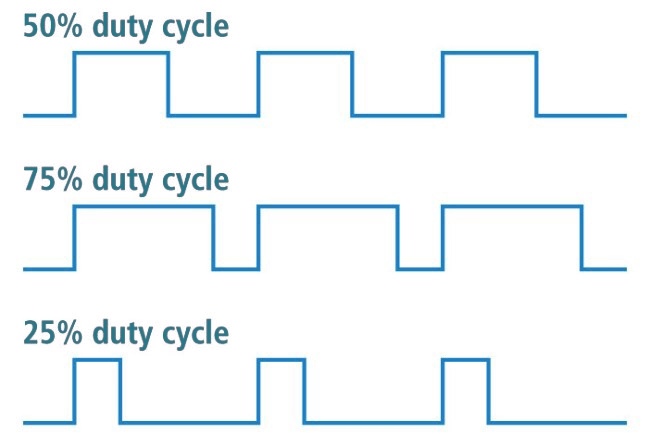
Don’t get me wrong, you can still achieve decent results with a high-end transformer welder, but your welding jobs can be much easier with an inverter welder. In addition, you can achieve much higher amps at a given duty cycle with an inverter welder. For example, most inverters have rated maximum output at 60% duty cycle, while transformers usually limit it to 20-30%.
Reliability and Durability
If you have read the first part of the article, you realize transformer welding machines take an edge when it comes to reliability and durability. Remember that transformer machines have proven reliable over time, so they will last more than you would expect if you maintain them regularly.
Meanwhile, the latest inverters are pretty reliable as the defects and failures from the early 1990s have been dealt with. However, working in dusty, dirty, and moist conditions may damage the internal components.
So if your welding jobs mostly revolve around the garage or indoor conditions, inverters will do just fine. However, if you need a workhorse capable of welding in more harsh conditions, you should opt for a transformer welder.
Costs
Like any new technology, inverter welding machines were significantly more expensive when they appeared on the market. However, high volume electronics manufacturing made them much cheaper and widespread, so the initial purchase cost between inverter and transformer welder today is similar.
Inverter welder will reduce the electricity costs, while transformer welder brings fewer maintenance costs after the warranty period. Downtime costs are debatable since certain applications can hurt inverter welder, but the repair costs can be somewhat higher.
Weight and Transportation
Since the inverters are significantly lighter and smaller, there is a simple rule when considering weight and transportation. If your projects require you to bring your job to your welder, you should opt for a transformer welder. On the contrary, you should go for an inverter welder if you get your welder to your job.
Resources:
- https://askforney.com/inverter-vs-transformer-welding-machines/
- https://www.thefabricator.com/thewelder/article/arcwelding/the-great-debate-transformers-or-inverters
- https://www.mig-welding.co.uk/forum/threads/inverter-vs-transformer.80045/
- https://forum.millerwelds.com/forum/welding-discussions/26672-transformers-vs-inverters-durability
- http://forum.weldingtipsandtricks.com/viewtopic.php?t=1282